5G NR and 4G LTE Comparison
A Short comparison of 5G and 4G technologies is given is table below
| Technology | Data Rates | Latency | Mobility Support | Spectrum Efficiency | Users Density | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5G (NR) | Avg 100 Mb/s Peak 20 Gb/s | ~ 1 ms | > 500 Km/h | x3 Better DL- 30 bits/Hz UL- 15bits/Hz |
1000K/square Km | x100 Better |
| 4G (LTE) | Avg 25 Mb/s Peak 300 Mb/s | ~10- 50 ms | Upto 350 Km/h | DL – 6 bits/Hz UL- 4 Bits/Hz | ~ 2K / square Km | Moderate |
5G New Radio and 4G LTE Parameter Level Comparison
| Parameter | 4G Long Term Evolution | 5G New Radio |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Long Term Evolution | New Radio |
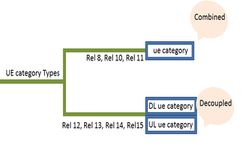
| 3GPP Release | Release 8 – Release 14 (LTE, LTE-A, LTE-Pro) | Release 15 onward |
| Frequency Range | < 6GHz | Upto 52.6 GHz |
| Services | Voice, MBB, IoT | Voice, eMBB, Low Latency Application, Massive IoT |
| Waveform |
|
|
| Max Carrier Bandwidth | 20 MHz |
|
| Subcarrier Spacing (SCS) | 15 KHz | 15 KHz, 30 KHz, 60 KHz, 120 KHz, 240KHz |
| Cylic Prefix (CP) | Normal CP; Extended CP |
|
| Max Number of Subcarriers Per Carrier |
1200 | 3300 |
| Radio Frame Length | 10 ms | 10 ms |
| Slot Size | 2/7/14 OFDM symbols | 1-14 OFDM symbols (including both slot & mini-slot) |
| UL/DL Ratio Change |
|
|
| Synchronization Signals |
|
|
| PBCH |
|
|
| SS -block Sweeping | 1 |
|
| RACH |
|
|
| MIMO Transmission |
|
|
| Reference Signals |
|
|
| Channel Coding |
|
|
| PDCCH |
|
|
| PUCCH |
|
|
| HARQ Round-trip Time | FDD: 9ms; TDD: ≥ 8ms | 0.25-16 ms |
| Wideband Operations |
|
|
| Mobility |
|
|
Table Source : Media-Tek White Paper
Related Post
- 5G Technology Requirements
- 5G – What Makes It Different & How Does It Impact Your Business
- 5G and 4G Comparison
- 5G NR (New Radio) Frequency Bands
- 5G Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (NR-ARFCN)
- 5G Cell Phone Architecture
- 5G/4G ARFCN Calculator Android App
- 5G mmWave Spectrum
- 5G Frequency Bands