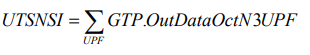5G End to End KPI – Accessibility, Integrity and Utilization
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a network is serving the user. In simple terms we can say KPIs describe the fitness level of a network, and this fitness level is measured with different matrix, e.g. when a doctor declare a Human being is fit and well, he measure his temperature, high blood pressure, high heart rate, blood sugar etc. similarly, network operates perform some measurement like network attach success rate, Average UL/DL data rate, Mobility success very famous for 4G/3Glegacy network to declare network as fit.
5G is quit new topic and as it will be covering too many uses cases, so we may expect new matrix to major the newtork KPIs and it is going to be a challenge for network operator while defining them. But if we see from the top, these KPI will under following categories.
- Accessibility
- Retainability
- Availability
- Mobility.
- Integrity
- Utilization
3GPP specification TS 28.554 has provided the definition for Accessibility, Integrity and Utilization.
Accessibility KPI
It is the probability that the user of a service after a request to a network receives the proceed-to-select signal within specified conditions. In 5G, successful registration to a network slice is the proceed-to-select signal to the UE. If users or subscribers cannot register to the network slice instance, they cannot access any network services in the network slice instance. This KPI is focusing on network view and following are the key matrix to measure accessibility KPI.
- Registered Subscribers of Network and Network Slice Instance through AMF:
-
- Name: Registered Subscribers of Single Network Slice Instance through AMF
- Description: It describe the total number of subscribers that are registered to a network slice instance
- Logical Formula definition: This KPI is obtained by counting the subscribers in AMF that are registered to a network slice instance.
- Physical formula definition:
-
![]()
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI: RegisteredAMFSubNbrMean
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Accessibility
- Unit of the KPI: Integer
- Type of the KPI: Cumulative measurement
-
- Registered Subscribers of Network and Network Slice Instance through UDM
-
- Name: Registered Subscribers of Single Network Slice Instance through UDM
- Description:This KPI describe the total number of subscribers that are registered to a network slice instance.
- Logical Formula definition:This KPI is obtained by counting the subscribers in UDM that are registered to a network slice instance.
- Physical formula definition:

- Measurement names used for the KPI: RegisteredSubUDMNbrMean
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Accessibility
- Unit of the KPI: Integer
- Type of the KPI: Cumulative measurement
-
- Registration success rate of one single network slice instance
-
- Name: Registration success rate of one single network slice instance
- Description:This KPI describes the ratio of the number of successfully performed registration procedures to the number of attempted registration procedures for the AMF set which related to one single network slice instance and is used to evaluate accessibility provided by the end-to-end network slice instance and network performance.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by successful registration procedures divided by attempted registration procedures.
- Physical Formula Definition:
-
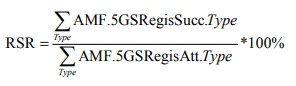
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI: AMF.5GSRegisAtt.Type, AMF.5GSRegisAttachSucc.Type
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Accessibility
- Unit of the KPI: Interger
- Type of the KPI: Cumulative measurement
- Measurement names used for the KPI: AMF.5GSRegisAtt.Type, AMF.5GSRegisAttachSucc.Type
-
- Accessibilty KPI Use Case: The no.of registered subscribers of single network slice instance can be used to describe the amount of subscribers that are successfully registered, it can reflect the usage of network slice instance. It is also useful to evaluate accessibility performance provided by one single network slice instance which may trigger the life cycle management (scale up, scale down etc.) of the network slice. This kind of KPI is valuable especially when network functions (e.g. AMF) are shared between different network slice instances. This KPI is focusing on both network and user view.
Integrity KPI
Integrity is the property that data have not been altered in an unauthorized manner and Service integrity is the degree to which a service is provided without excessive impairments, once obtained.
- Downlink latency in gNB-DU
-
- Name: Downlink latency for IP packets through gNB in split scenario
- Description:This KPI describes the gNB-DU part of the packet transmission latency experienced by an end-user. It is used to evaluate the gNB latency contribution to the total packet latency.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is the average (arithmetic mean) of the time from reception of IP packet to gNB-DU until transmission of first part of that packet over the air interface, for a packet arriving when there is no previous data in queue for transmission to the UE
- Physical Formula Definition:
-
![]()
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI: DRB.RlcSduLatencyDl, DRB.RlcSduLatencyDl.QoS,
- KPI Object: NG-RAN
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI:Time interval (millisecond)
- Type of the KPI:MEAN
- gNB-DU Latency KPI User Case: The end-to-end latency is an important performance parameter for operating 5G network. In some scenarios (e.g. uRLLC), if end-to-end latency is insufficient, the 5G network customer cannot obtain guaranteed network performance provided by the network operator. So it is necessary to define end-to-end latency of network related measurement to evaluate whether the end-to-end latency that network customer requested has been satisfied. A procedure is invoked by network management system and is used:
-
-
-
- To update the CSMF/NSMF with the end-to-end latency parameter for monitoring;
- To inform the network customer/network operator the end-to-end latency;
- To make CSMF/NSMF aware if the end-to-end latency can meet network customer’s service requirement.
- If high end-to-end latency are measured, it is also of benefit to pinpoint where in the chain from application to UE that the latency occurs.
-
- Upstream Throughput for Network and Network Slice Instance
-
- Name: Upstream throughput for network and network slice instance
- Description:This KPI describes the upstream throughput of one single network slice instance by computing the packet size for each successfully transmitted UL IP packet through the network slice instance during each observing granularity period and is used to evaluate integrity performance of the end-to-end network slice instance.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by upstream throughput provided by N3 interface from NG-RAN to UPF which is related to the single network slice instance.
- Physical Formula Definition:
-

-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI:GTP.InDataOctN3UPF
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI:Kbit/s
- Type of the KPI: Cumulative measurement
-
- Downstream Throughput for Single Network Slice Instance
-
- Name: Downstream throughput for network and network slice instance.
- Description:This KPI describes the downstream throughput of one single network slice instance by computing the packet size for each successfully transmitted DL IP packet through the network slice instance during each observing granularity period and is used to evaluate integrity performance of the end-to-end network slice instance.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by downstream throughput provided by N3 interface from NG-RAN to UPF which is related to the single network slice instance.
- Physical Formula Definition:

-
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI:GTP.OutDataOctN3UPF
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI: Kbit/s
- Type of the KPI: Cumulative measurement
-
- Upstream Throughput at N3 interface
-
- Name: Upstream GTP data throughput at N3 interface
- Description: This KPI describes the total number of octets of all incoming GTP data packets on the N3 interface (measured at UPF) which have been generated by the GTP-U protocol entity on the N3 interface, during a granularity period. This KPI is used to evaluate upstream GTP throughput integrity performance at the N3 interface.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by measuring the GTP data upstream throughput provided by N3 interface from NG-RAN to UPF, during the granularity period.
- Physical Formula Definition:
-
![]()
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI:GTP.InDataOctN3UPF
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI: Kbit/s
- Type of the KPI: MEAN
-
- Downstream Throughput at N3 interface
-
- Name: Downstream GTP data throughput at N3 interface.
- Description:This KPI describes the total number of octets of all downstream GTP data packets on the N3 interface (transmitted downstream from UPF) which have been generated by the GTP-U protocol entity on the N3 interface, during a granularity period. This KPI is used to evaluate integrity performance at N3 interface.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by measuring the GTP data downstream throughput provided by N3 interface from UPF to NG-RAN, during the granularity period.
- Physical Formula Definition:

- Measurement names used for the KPI:GTP.OutDataOctN3UPF
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI: Kbit/s
- Type of the KPI: MEAN
- Throughput KPI Use Case: Measuring throughput is useful to evaluate system load of end to end network slice. If the throughput of the specific network slice instance cannot meet the performance requirement, some actions need to be performed to the network slice instance e.g. reconfiguration, capacity relocation. So it is necessary to define the IP throughput for one single network slice instance. This KPI is focusing on network and user view.
-
- RAN UE Throughput
-
- Name: RAN UE Throughput.
- Description: A KPI that shows how NG-RAN impacts the service quality provided to an end-user
- Logical Formula Definition:Payload data volume on RLC level per elapsed time unit on the air interface, for transfers restricted by the air interface.
- Physical Formula Definition:

-
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI:DRB.UEThpDl, DRB.UEThpUl, DRB.UEThpDl.QoS, DRB.UEThpUl.QoS
- KPI Object: NG-RAN
- KPI category: Integrity
- Unit of the KPI: Kbit/s
- Type of the KPI: MEAN
- UE Throughput KPI Use Case:The UE perceived throughput in NG-RAN is an important performance parameter for operating 5G network. If the UE throughput of the NR cell cannot meet the performance requirement, some actions need to be performed to the network, e.g. reconfiguration or capacity increase. So it is necessary to define UE throughput KPI to evaluate whether the endusers are satisfied. The KPI covers volume large enough to make the throughput measurement relevant, i.e. excluding data volume of the last or only slot.
- The UE throughput KPI covers also “NR option 3” scenarios. Then the gNB is “connected” towards the EPC, and not towards 5GC. It is proposed to allow the KPI separated based on mapped 5QI (or for QCI in case of NR option 3). When network slicing is supported by the NG-RAN, multiple Network Slice Instances may be supported. The UL and DL UE throughput for each NSI (NSI) is then of importance to the operator to pinpoint a specific performance problem.
-
Utilization KPI
- Mean number of PDU sessions of network and network Slice Instance
-
- Name: Mean number of PDU sessions of Single Network Slice Instance.
- Description: This KPI describes the mean number of PDU sessions that are successfully established in a network slice instance.
- Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by successful PDU session establishment procedures of SMFs which is related to the network slice instance.
- Physical Formula Definition:
-
![]()
-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI: PDUSessionNum
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Utilization
- Unit of the KPI: Erlang
- Type of the KPI: MEAN
- KPI Use Case: It is necessary to evaluate the mean PDU session number in the network slice instance to indicate system load level. For example, if the mean value of the PDU sessions is high, maybe the system capacity should be increased. This KPI is focusing on network view.
-
- Virtualised Resource Utilization of Network Slice Instance
-
- Name: Virtualised resource utilization of single network slice instance
- Description: This KPI describes utilization of virtualization resource (e.g. processor, memory, disk) that are allocated to a
network slice instance. - Logical Formula Definition: This KPI is obtained by the usage of virtualization resource (e.g. processor, memory, disk) divided by the system
capacity that allocated to the network slice instance. - Physical Formula Definition:
-

-
-
- Measurement names used for the KPI: MeanProcessorUsage, MeanMemoryUsage, MeanDiskUsage, System capacity indicates amount of virtualised resource which allocated to the network slice instance.
- KPI Object: 5GS
- KPI category: Utilization
- Unit of the KPI:Percentage
- Type of the KPI:Ratio
- Utilization KPI Use Case: It is necessary to evaluate the current utilization of virtualised resources (e.g. memory and storage utilization) that a network slice instance is occupied. If the utilization is larger or smaller than the threshold, maybe some scale in/out operations will be made by the management system. This KPI is focusing on network and user view.
-
Related Post
- 5G Channel Modes: Requirements and Deployment Scenarios
- 5G Self Backhaul- Integrated Access and Backhaul
- 5G Transport Network Requirement for Indian Telecom
- 5G NG Identities (UE and Network Identifiers)
- 5G NR Radio Protocol Stack (Layer 2 and Layer 3)