5G Global Unique Temporary Identifier [5G – GUTI] is a core network temporary identifier and allocated by Access and Mobility Management function [AMF] to the UE.
- GUTI is 80 bits long core network identifier
- It is consist of major three network identities PLMN + AMF ID + TMSI
- It is a temporary identifier so it’s associations is not fixed to a specific subscriber or mobile
- Single 5G-GUTI can be used for accessing 3GPP and non-3GPP technologies security context within the AMF
- An AMF may re-assign a new 5G-GUTI to the UE at any time under specified conditions
- When the UE is in CM-IDLE, the AMF may delay in the assignment of a new 5G-GUTI until the next NAS transaction happens
When AMF provides a New 5G-GUTI
- Upon receiving Registration Request message of type “initial registration” or “mobility registration update” from a UE, the AMF shall send a new 5G-GUTI to the UE in Registration Accept message
- Upon receiving Registration Request message of type “periodic registration update” from a UE, the AMF should send a new 5G-GUTI to the UE in Registration Accept message
- Upon receiving network triggered Service Request message from the UE (i.e., Service Request message sent by the UE in response to a Paging message), the AMF shall use a UE Configuration Update procedure to send a new 5G-GUTI to the UE
Exceptions
- It is left to implementation to re-assign 5G-GUTI more frequently than in cases mentioned above
- It is left to implementation to generate 5G-GUTI containing 5G-TMSI that uniquely identifies the UE within the AMF
5G GUTI Structure
Globally Unique AMF ID (GUAMI) Structure (48 bits)
- AMF Region ID addresses the case that there are more AMFs in the network than the number of AMFs that can be supported by AMF Set ID and AMF Pointer by enabling operators to re-use the same AMF Set IDs and AMF Pointers in different regions
S-TMSI Structure (48 bits)
S-TMSI is the shortened form of the GUTI to enable more efficient radio signalling procedures e.g. during Paging and Service Request and its structure is shown below.
- In NG-RAN uses the 10 Least Significant Bits of the 5G-TMSI in the determination of the time at which different UEs are paged. Hence, the AMF shall ensure that the 10 LSB of the 5G-TMSI are evenly distributed
5G and 4G GUTI Mapping
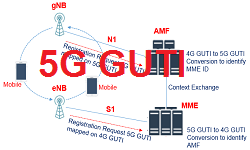
3GPP has speficied a mapping between 5G-GUTI and 4G-GUTI. This mapping is required for UE mobility between 4G and 5G networks. For example, when a Mobile User moves from 5G to 4G, it requires to send a GUTI to MME, then mobile has to map the 5G-GUTI onto thw 4G-GUTI and forward it to MME. MME perform a reverse mapping of 4G GUTI to 5G-GUTI to find out the AMF from where the MME needs to contact to fetch the UE context.
In similar way, when a mobile moves from 4G to 5G, mobile maps and send 4G GUTI to AMF and AMF decode the MME ID for retrieve the User context. Below figure show the mapping and bit wise detailed information for 5G and 4G GUTI.
References:
- 3GPP TS 23.501, System architecture for the 5G System
- 3GPP TS 33.501, Security architecture and procedures for 5G System
Related Post