5G NR Radio Protocol Stack (Layer 2 and Layer 3)
3GPP has released specification 38.300 V1 this month about NR and NG-RAN Overall Description: Stage 2, This standard comes with the detailed descriptions about 5G NR network and Protocol architecture.
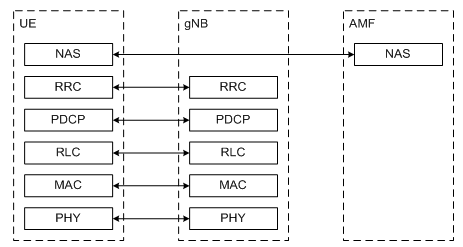
NR Radio User plane and Control Protocol Stack is shown in below figures:
Figure #1 User Plane Protocol Stack Figure #2 Control Plane Protocol Stack
When we closely see both the protocol stack we could see many similarities between LTE protocol stack and 5G-NR protocol stack because LTE protocol stack is being taken as the base line for the development 5G-NR.
5G-NR User plane contains Phy, MAC, RLC, and PDCP same as LTE and has introduced a new layer named as SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol).
On another side, the control plane of 5G-NR is identical to LTE, here MME equivalent node named as AMF (Access and Management Mobility Function).
5G-NR Layer 3 (RRC) Functions:
The main services and functions of the RRC sub layer include:
- Broadcast of System Information related to AS and NAS;
- Paging initiated by 5GC or NG-RAN;
- Establishment, maintenance, and release of an RRC connection between the UE and NG-RAN including Addition, modification, and release of carrier aggregation, Addition, modification, and release of Dual Connectivity in NR or between E-UTRA and NR.
- Security functions including key management;
- Establishment, configuration, maintenance, and release of Signalling Radio Bearers (SRBs) and Data Radio Bearers (DRBs);
- Mobility functions including Handover and context transfer; UE cell selection and reselection and control of cell selection and reselection; Inter-RAT mobility.
- QoS management functions;
- UE measurement reporting and control of the reporting;
- Detection of and recovery from radio link failure;
- NAS message transfer to/from NAS from/to UE.
5G-NR Layer 2 Functions:
The layer 2 of NR is split into the following sub layers:
- Service Data Adaptation Protocol (SDAP)
- Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP)
- Radio Link Control (RLC)
- and Medium Access Control (MAC)
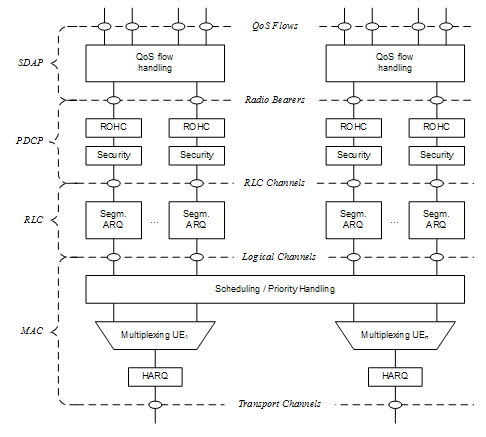
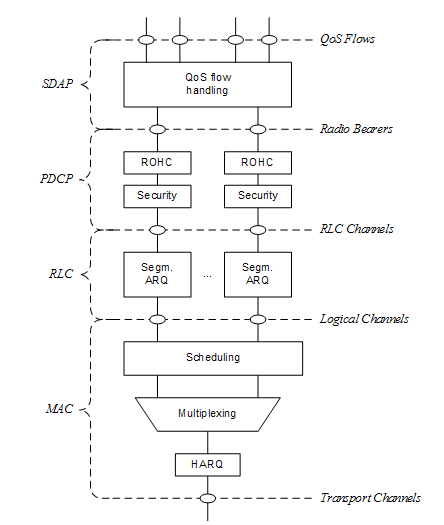
The two figures below depict the Layer 2 architecture for downlink and uplink, where:
- The physical layer offers to the MAC sublayer transport channels;
- The MAC sub layer offers to the RLC sublayer logical channels;
- The RLC sub layer offers to the PDCP sublayer RLC channels;
- The PDCP su blayer offers to the SDAP sublayer radio bearers;
- The SDAP su blayer offers to 5GC QoS flows;
- Comp. refers to header compression and segm. to segmentation;
- Control channels (BCCH, PCCH are not depicted for clarity).
Figure #3 Downlink Layer 2 Structure Figure #4 Uplink Layer 2 Structure
SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol) Protocol Functions :
The main services and functions of SDAP include:
- Mapping between a QoS flow and a data radio bearer (Due to new QoS framework)
- Marking QoS flow ID (QFI) in both DL and UL packets ( DL: due to reflective QoS and UL: due to new QoS framework)
A single protocol entity of SDAP is configured for each individual PDU session, except for DC where two entities can be configured.
PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) Layer Functions:
The main services and functions of the PDCP sublayer for the user plane include:
- Sequence Numbering
- Header compression and decompression: ROHC only
- Transfer of user data
- Reordering and Duplicate detection (if in order delivery to layers above PDCP is required)
- PDCP PDU routing (in case of split bearers)
- Retransmission of PDCP SDUs
- Ciphering and Deciphering
- PDCP SDU discard
- PDCP re-establishment and data recovery for RLC AM
- Duplication of PDCP PDUs
The main services and functions of the PDCP sublayer for the control plane include:
- Sequence Numbering;
- Ciphering, deciphering and integrity protection;
- Transfer of control plane data;
- Duplicate detection;
- Duplication of PDCP PDUs.
RLC (Radio Link Control ) Layer Functions:
The main services and functions of the RLC sublayer depend on the transmission mode and include:
- Transfer of upper layer PDUs
- Sequence numbering independent of the one in PDCP
- Error Correction through ARQ
- Segmentation and re-segmentation
- Reassembly of SDU
- RLC SDU discard
- RLC re-establishment
Note: no concatenation and no reordering
MAC (Media Access Control) Layer Functions
The main services and functions of the MAC sub layer include:
- Mapping between logical channels and transport channels
- Multiplexing/demultiplexing of MAC SDUs belonging to one or different logical channels into/from transport blocks (TB) delivered to/from the physical layer on transport channels
- Scheduling Information Reporting
- Error correction through HARQ
- Priority handling between UEs by means of dynamic scheduling
- Priority handling between logical channels of one UE by means of logical channel prioritization
- Padding
A single MAC entity can support one or multiple numerologies and/or TTI durations and mapping restrictions in logical channel prioritization controls which numerology and/or TTI duration a logical channel can use.
Related Post:
- 5G Network Sharing: Concept, Benefits and Architectures
- Hybrid Core Network – 4G Core to 5 G Core Interconnection
- Deployments Scenarios for 5G-NR
- 5G Key Performance Indicator Definitions Template by 3GPP
- 5G End to End KPI – Accessibility, Integrity and Utilization