SSC Modes – Session and Service Continuity in 5G
In any telecom technology one of the key feature requirement is data session and service continuity to enusre the uninterrputed service experience to the users irrespective of any change of UE IP address or change in Core network achor point. In 4G, EPC provides the continutiy of IP session by maintaining the P-GW and UEs PDU session IP regradless of UE’s mobility.
In 5G system architecture, Session and Service Continuity (SSC) support enables to address the various continuity requirements for different applications and services for the UE. However, not all applications require guaranteed IP session continuity even if service continuity is needed but 5G being more flexibility and evolved, offers different types of session continuity depending on UE or service type.
Key Pointer for SSC Modes
- 5G technique allows the service provider to set a specific SSC mode for a given PDU Session
- SSC Modes determines the flow of the packets across network in mobility scenarios
- A PDU Session is configured to use a specific ‘Session and Service Continuity’ (SSC) mode
- 3GPP specification provided three different types of SSC modes
- UE can request a specific mode using the ‘SSC Mode‘ field within the NAS: PDU Session Establishment Request
- The SMF specifics the allocated mode using the ‘Selected SSC Mode‘ field within the NAS: PDU Session Eslablishment Accept
- SSC Mode 1 & 2 can work for PDU Type as IP and Ethernet where as SSC Mode 3 can be only work with PDU session type as IP
Types of SSC Modes
5G System architecture provides three types of Session and Service Continuity (SSC) modes to addresses various continuity requirements of different applications/services. Once an SSC mode is associated with a PDU Session then it does not change during the lifetime of the PDU Session. The 5G architecture allows applications to influence the selection of SSC modes as needed for required data service and shown in following figure.

- SSC Mode 1: With SSC mode 1, the 5G network preserves the connectivity service provided to the UE. For the PDU session Type as IPv4 or IPv6 or IPv4v6 type, the IP address is preserved. In this case the User Plane function (UPF) acting as the PDU session anchor is maintained (remains same) till the point UE release the PDU session.
- SSC Mode 2: With SSC mode 2, the 5G network may release the connectivity provided to the UE, i.e. the PDU Session can be released. If the PDU Session is being used to transfer IP packets, then the allocated IP address is also released. An usecase for this is a network may release connectivity if there is a requirement for load balancing at the anchor UPF. Here, the PDU Session may be moved onto a different anchor UPF by releasing the existing PDU Session and subsequently establishing a new PDU Session. It works on break and make framework i.e. PDU session will be release from first serving UPF and then a new PDU session is established at new UPF.
- SSC Mode 3: With SSC mode 3, the network preserves the connectivity provided to the UE but there may be some impact during certain procedures. For example, the IP address allocated to the UE will be updated if the Anchor UPF changes but the change procedure will ensure that connectivity is preserved, i.e. connectivity towards the new Anchor UPF is established before releasing the connection to the old Anchor UPF. The 3GPP release 15 only supports Mode 3 for IP based PDU Sessions.
How does Session and Service Continuity Mode Selection Works?
The SSC mode selection policy is used to determine the type of session and service continuity mode associated with an application or group of applications for the UE. A MNO may provision the policy rules for UE to determine the type of mode associated with an application or a group of applications. There can be a default policy that matches all applications on UE.
When a UE initiates a PDU session it determines the which SSC mode it has to use for a particular application by checking SSC mode selection policy and included it within PDU session establishment request as “SSC mode” IE. In 5G Core, the SMF can recieve the list of supported SSC modes and the default SSC mode per DNN per S-NSSAI as part of the subscription information from the UDM. The SMF select the SSC mode by checking against subscriber data and local SMF configuration and allowed SSC mode.
Based on selection results, the SMF can either accepts or modifies or rejects based on UE subscription or local configuration. If UE does not provide SSC, then SMF selects default SSC depending on the data network in subscription or local configuration.
Call Flow for SSC Mode Information:
The SSC mode information is exchanged as part of NAS layer signalling as shown below. The UE sends the PDU session establishment request including the PDU session type and request SSC mode (Optional) toward the Core Network. The Core network response the Selected SSC mode as part of PDU session establishmet accept.
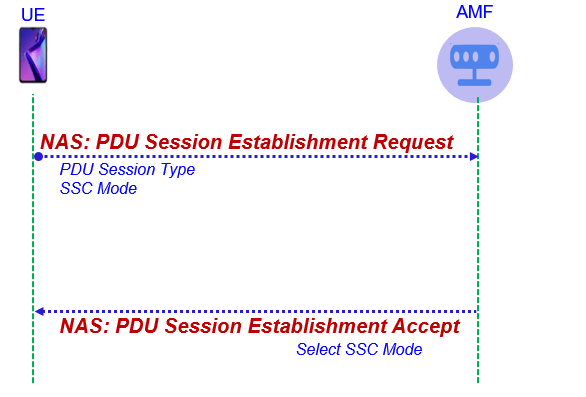
PDU Session Establishment Request

PDU Session Establishment Accept

References:
- 3GPP TS 23.501 5G; System Architecture for the 5G System
Related Posts:
- 5G NAS Authentication Failures Cause Values
- 5G NAS Registration Reject Cause
- 5G NAS PDU Session Reject Cause Values and Reasons
- 5G NR Global Unique Temporary Identifier (GUTI)
- 5G PDU Session and Its Types