PSS and SSS (LTE Synchronization)
PSS and SSS (LTE Synchronization)
After power-up, the UE tries to obtain time and frequency synchronization with the system. For this, UE needs to detect signals to find out where the frame begins and ends. LTE define two type of synchronization signals:
- Primary synchronization signal (PSS)
- Secondary synchronization signal (SSS)
UE uses the Synchronization Signals to:
- Achieve radio frame, subframe, slot and symbol synchronization in the time domain
- Identify the center of the channel bandwidth in the frequency domain
- Deduce the Physical layer Cell Identity (PCI)
Primary Synchronization Signals:
Primary synchronization signals consist of one of three 62-symbol Zadoff-chu sequences in a cell.
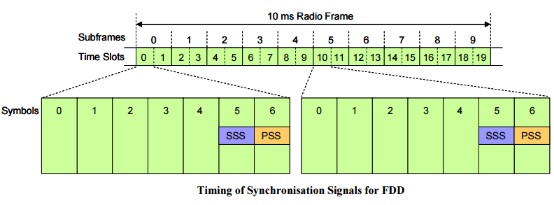
The Primary Synchronization Signal (PSS) is broadcast twice during every radio frame and both transmissions are identical.
In the case of FDD: the PSS is broadcast using the central 62 subcarriers belonging to the last symbol of time slots 0 and 10 «
In the case of TDD: the PSS is broadcast using the central 62 subcarriers belonging to the third symbol of time slot 2 (subframe 1) and the third symbol of time slot 12 (subframe 6)
PSS helps to achieve subframe, slot and symbol synchronization in the time domain, identify the center of the channel bandwidth in the frequency domain and deduce a pointer towards 1 of 3 Physical layer Cell Identities (PCI).
The PSS cannot be used to achieve radio frame synchronization because both transmissions within the radio frame are identical and equally spaced in time.
Secondary Synchronization Signals:
After the primary sync signal acquisition, UE tries to detect the secondary synchronization signal. Secondary synchronization signals are one of 168 codes which are 62-bit sequences. The Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS) is broadcast twice within every radio frame. The two transmissions of the SSS are different so the UE can detect which is the first and which is the second
In the case of FDD: the SSS is broadcast using the central 62 subcarriers belonging to the second to last symbol of time slots 0 and 10 «
In the case of TDD: the SSS is broadcast using the central 62 subcarriers belonging to the last symbol of time slot 1 (subframe 0) and the last symbol of time slot 11 (subframe 5)
SSS helps to achieve radio frame synchronization and deduce a pointer towards 1 of 168 Physical layer Cell Identity (PCI) groups.
Below diagram shows how PSS and SSS helps finding the Physical Layer Cell ID.
Related Posts:
- LTE eNodeB Schedulers and Different Scheduling Types
- LTE EUTRAN Bands
- Feature Group Indicators (FGI bits) in LTE Rel. 8, Rel. 9, Rel. 10
- Dual Connectivity (DC) Definition, Protocol Architecture, DC and CA Comparison
- Multi Carrier Cell Reselection in LTE
- Maximum Coupling Loss (MCL) and Maximum Path Loss (MPL)