Narrow Band IoT Frame Structure
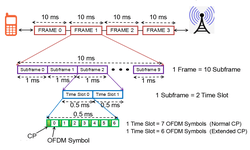
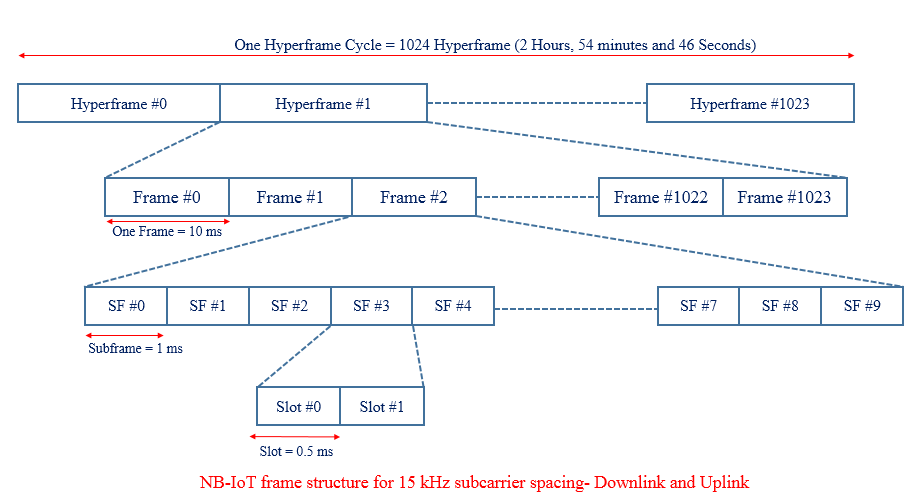
NB- IoT frame structure is illustrated in below picture. At the highest level, it starts with hyperframe cycle where one hyperframe cycle has 1024 hyperframes and each consisting of 1024 frames.
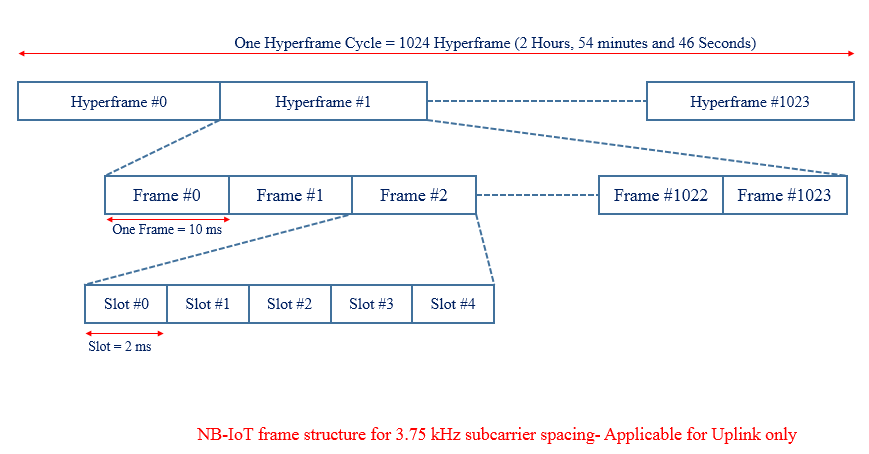
One frame consists of 10 sub-frames and each subframe is dividable into two slots each of 0.5 ms which is similar to traditional LTE system. In the DL and UL, the NB-IoT design supports a sub-carrier spacing of 15 KHz, for which each frame contains 20 slots. In the UL, the NB-IoT design supports an additional sub-carrier spacing of 3.75 KHz. For this alternative sub-carrier spacing, each frame is directly divided into five slots, each of 2 ms, there is not subframe concept.
Case #1 Downlink and Uplink Subcarrier Spacing 15KHz
Case #2 Uplink Subcarrier Spacing 3.75 KHz
Notation and Range:
- Hyperframe: Hyper System Srame Number (H-SFN), Range : 0 – 1023
- Frame System Frame Number (SFN), Range : 0 – 1023
- Subframe: Subframe Number (SN), Range : 0 – 9
Each subframe can therefore be uniquely identified by an H-SFN, an SFN, and a subframe number (SN).
Cycle Duration:
- Duration of a Frame cycle =(No. of Frame in one cycle) x (Duration of one frame) = 1024 x 10 ms =10240 ms = 10.24 seconds
- Duration of a Hyperframe cycle = (No. of Hyperframe in one cycle) x (Duration of one Hperframe) = 1024 x 10.24 s =104857.60 ms = 2 Hours, 54 minutes and 46 seconds
Related Post:
- Narrow Band IoT
- Narrow Band IoT Frequency Bands
- Narrow Band IoT Frame Structure
- Narrow Band Synchronization Signals (NPSS and NSSS)
- NB-IoT PRBs (Physcial Resource Blocks) for In-Band Operation
- Narrow Band IoT- Signalling Radio Bearers (SRBs)
- Narrow Band-IOT UE Attach Call Flow Messaging
- Cat. NB1 and Cat. NB2 Devices Comparison