CBRS Network Architecture and Spectrum Access System Operation
CBRS Network Architecture:
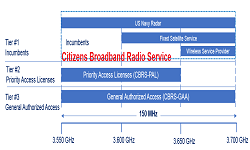
CBRS is known as Citizen broadband radio service, It is a 150 MHz wide broadcast band in 3.5 GHz band starting from 3550 MHz to 3700 MHz. In 2017, the FCC completed a process to establish rules for commercial use of this band. Commercializing this band enables Service Providers/Wireless Operators to use it without acquiring frequency licenses. CBRS frequency spectrum shall help 4G/5G mobile networks deployment quicker and easier. CBRS band is also referred as 3.5 GHz band.
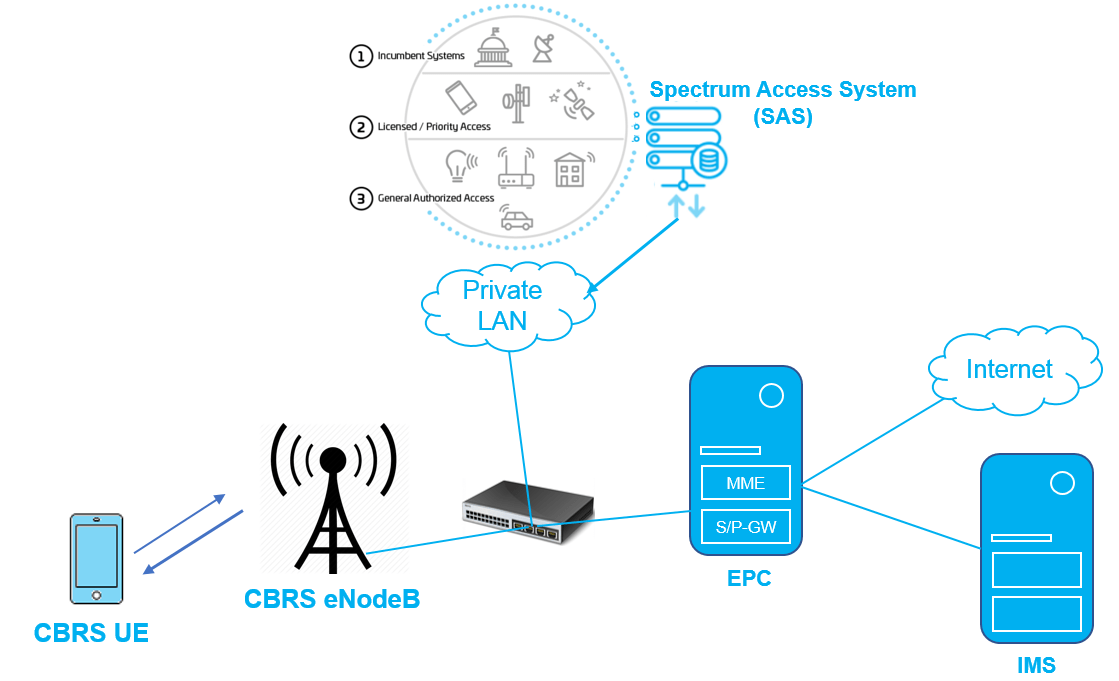
Considering CBRS is deployed with 4G LTE technology, it is very much similar to LTE network where we have a 4G eNodeB, Core Network for Packet services and IMS for voice and multimedia service. A CBRS network is shown in below picture. An eNodeB which is capable to support CBRS band is referred as Citizens Broadband Radio Service Device. CBSD devices are categorized into two types:
- CBSD-Category A
- CBSD-Category B
while comparing CBRS network with traditional LTE network we can see an additional node known Spectrum Access System (SAS). SAS is a three-tier spectrum authorization framework to accommodate a variety of commercial uses on a shared basis with incumbent federal and non-federal users of the CBRS band. It is conceptually similar to the databases used to manage Television White Space (TVWS) devices.
The three tiers licenses Managed by Spectrum Access System :
- Incumbent Access (IA): This access license is used by the US Navy users and also for fixed satellite services (FSS). This access has absolute priority over other type of allocation.
- Priority Access (PA): This license is used by hospitals, utilities and government departments as well as non-critical users such as mobile network operators (MNOs).This access license will be assigned using competitive bidding within the 3550-3650 MHz frequency block. Each license under this is defined as a non-renewable authorization to use a 10 megahertz channel in a single census tract (small geographic area- district) for three-years. Up to seven total PALs may be assigned in any given census tract with up to four PALs going to any single applicant. Applicants may acquire up to two-consecutive PAL terms in any given license area during the first auction.
- General Authorized Access (GAA): This is for users that will potentially have access to all 150 megahertz in the 3550-3700 MHz. General Authorized Access users are permitted to use any portion of the 3550-3700 MHz band not assigned to a higher tier user and may also operate opportunistically on unused Priority Access channels.
Spectrum Access System (SAS) Interface and Operation
SAS – CBSD interface is based on the HTTP over Transport Layer Security (HTTP-TSL). The SAS-CBSD interface exchanges the following messages for the operation:
- CBRS eNodeB (CBSD) Registration Request/Response
- Spectrum Inquiry Request/Response
- Grant Request/Response
- Heartbeat Request/Response
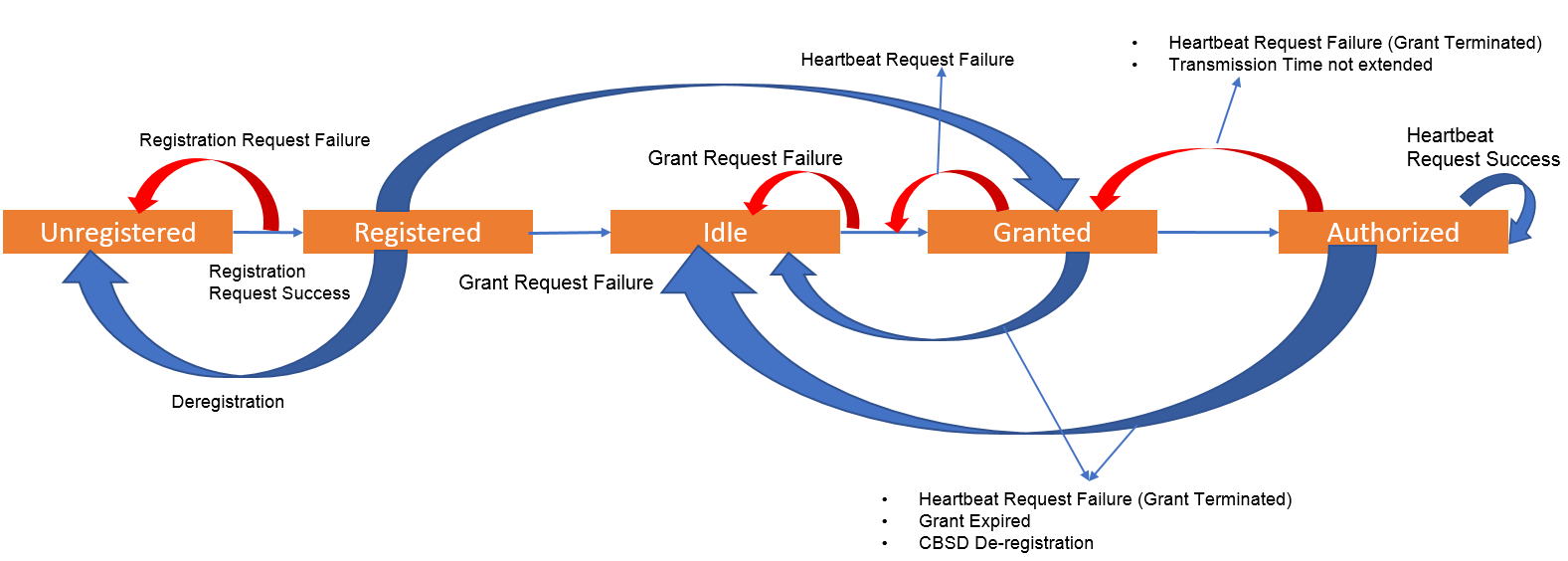
When CBRS eNodeB gets powered on, it start the SAS-CBSD registration procedure with the SAS to gain access to the spectrum. It sends the registration request with all mandatory parameters required by the SAS. After successful registration, it performs a spectrum inquiry for the available channel information from the CBRS band. Upon success of the spectrum inquiry, the CBRS eNodeB sends a grant request with one of the operating channels and peak power is received in the spectrum inquiry response.
The spectrum inquiry is an optional procedure. In case of an inquiry failure, the CBRS eNodeB continues with grant procedure.In response to the grant request, the eNodeB gains approval for the requested frequency channel and peak transmit power. It also receives the time period for the grant. Once the CBRS eNodeB reaches the granted state, it initiates a heartbeat procedure and takes authorization from the SAS for RF transmission.
On the reception of the first successful heartbeat response from the SAS, the CBRS eNodeB starts radiating. Figure below depicts the state flow of the SAS-CBRS eNodeB procedures based on different events. The granted state means the CBRS eNodeB is as good as a standard LTE eNodeB and can perform all LTE functionalities.
Reference :
- Aricent White Paper