What is BTS, Which unit of BTS consumes most of the power ?
A base transceiver station (BTS) is a piece of equipment that facilitates wireless communication between user equipment (UE) and a network. UEs are devices like mobile phones (handsets), computers with wireless Internet connectivity. The network can be that of any of the wireless communication technologies like GSM, CDMA, Wi-Fi, LTE, 5G or other wide area network (WAN) technology
BTS is also referred to as the radio base station (RBS), node B (in 3G Networks) or, simply, the base station (BS). For discussion of the LTE standard the abbreviation eNB for evolved node B is widely used.
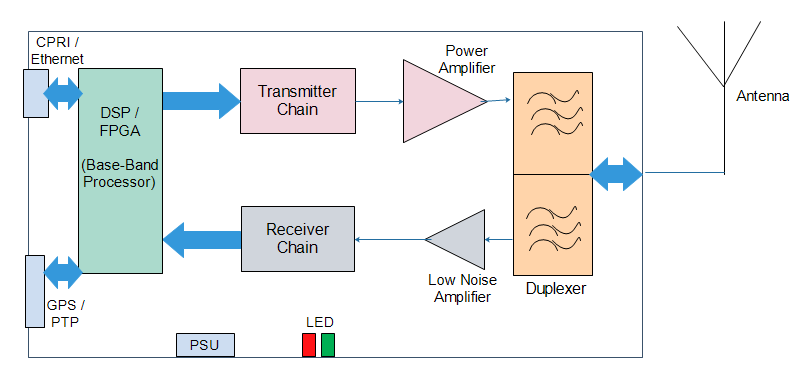
A BTS is usually composed of:
Transceiver (TRX)
Transceiver consists of transmitter and receiver chain radio chain. Transmitter chain converts digital data to analog data, upconvert to radio frequency, and support other functions such as filtering and amplification etc. Receiver chain takes data from antenna, amplifies it, downconvert and finally it converts analog data to digital data.
Power amplifier (PA)
Amplifies the signal from transmitter chain for transmission through antenna to the high power levels.
Duplexer
A duplexer typically consists of two band pass filters connected in parallel. One filter provides a path between the transmitter and the antenna, the other provides a path between the antenna and the receiver. No direct path between the transmitter and receiver exists.
Antenna
This is the structure that the BTS lies underneath; it can be installed as it is or disguised in some way (Concealed cell sites).
PSU
This is power supply unit of BTS. It generally takes -48V DC supply as input and supplies power to the other parts of the BTS.
Control function
Controls and manages the various units of BTS, including any software. On-the-spot configurations, status changes, software upgrades, etc. are done through the control function.
Baseband unit
It performs the digital processing of the signal, encoding, decoding etc.
Most power consuming unit in BTS
Power amplifier unit of the BTS consumes most of the power consumed by BTS. Here is the example calculating power consumed by power amplifier out of total BTS power consumed.
Suppose, BTS is single TRX (means 1 TX, 1 RX), and it consumes around 140W.
Output power of BTS at antenna port = 10W (40dBm)
Output power of BTS at Power Amplifier (PA) Output port = 20W (43dBm) ; Considering 3dB loss of duplexer after the PA.
PA efficiency (approx.) = 25%
Power consumed by PA = PA output power / Efficiency
= 20W / 0.25
= 80W
So, 80W power is consumed by PA only, out of 140W total power consumed by BTS. And rest 60W is used by transceiver part, base-band part etc.
Efforts are being made to increase the efficiency of the PA and also there are some techniques already available,, such as Doherty Amplifier configuration, Envelop Tracking etc.