5G SON | Automatic Neighbor Relations | ANR
Introduction
In old days, 2G and 3G Cellular systems configurations were based on information from planning tools and drive tests. With the development of 4G LTE, the Service Providers put the requirements for management simplicity and cost efficiency. This put a great focus for creating solutions for Self-Organizing Networks (SON). One of the first SON solutions introduced in the standards was the Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR), to automatically generate neighbor relations between Base Station Cells. These relations are used to establish connections Base Station Cells to support mobility, load balancing, dual connectivity, etc.
With 4G deployments, we have seen ANR significantly reduced the planning and operation costs for operators. Therefore, 3GPP considered automatic establishment of neighbor relations also very important in 5G NR . In this blog post we will discuss the basics of ANR with respect to 5G NR.
ANR Key Pointers
- ANR enable to generate automatically neighbor relations between Base Station Cells and neighboring Base Stations Cells
- ANR neighbor relation helps in supporting the mobility, load balancing and dual connectivity
- ANR function manages the conceptual Neighbor Relation Table (NRT)
- ANR neighbor detection function finds new neighbors and adds them to the NRT
- ANR neighbor removal function removes outdated neighbor from the NRT
3GPP ANR Functional Architecture
Figure below shows, ANR Functional Architecture as per 3GPP LTE specifications and also relevant to 5G NR also. It shows interactions between the Base Station and O&M for ANR operation.
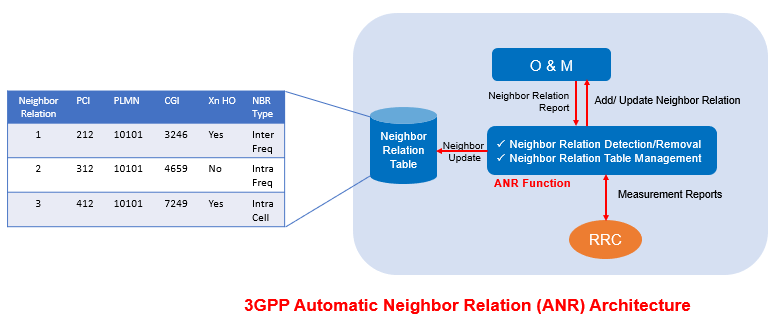
The ANR function resides in the gNodeB and manages the conceptual Neighbor Relation Table (NRT). In ANR, the neighbor detection function finds new neighbors and adds them to the NRT and the neighbor removal function removes outdated neighbor relations (NRs) . The neighbor detection and neighbor removal function’s implementation is not defined by 3GPP specification, it is vendor specific.
An existing Neighbor cell Relation (NR) from a source cell to a target cell means that gNodeB controlling the source cell knows the NCGI/CGI and Physical Cell Identity (PCI) of the target cell and has an entry in the NRT for the source cell identifying the target cell. For each cell that the gNodeB keeps a NRT containing the Target Cell Identifier to identify the target cell. For 5G New Radio, the Target Cell Identifier corresponds to the NR- Cell Global Identifier (NCGI) and Physical Cell Identity (PCI) of the target cell.
The ANR function relies on cells broadcasting their identity at global level, NR Cell Global Identifier (NR-CGI) with in SIB#1 and allows O&M to manage the NRT. O&M can add and delete neighbor relations and can also change the attributes of the NRT.
Types of Neighbor Relation
5G Can be deployed with two architectures – Non Stand Alone (NSA) and Stand Alone (SA), based on this we can have different type of neighbors relation presented in following blog post.
Signal and Identifiers for ANR Use
For UE based ANR SSB (Synchronization Signal Block) and SIB#1 also know as RMSI (Remaining Minimum System Information) are most critical signal and information block. SSB and SIB#1 carries the required information to populate the Neighbor relations i.e. PCI and NCGI (New Radio Cell Global Identifier).
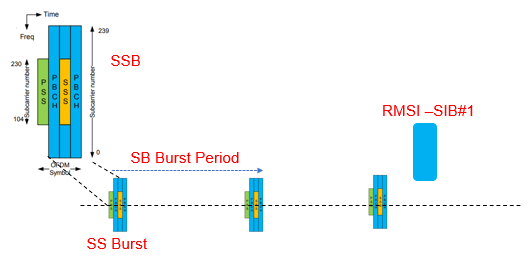
When UE search signals for neighboring cells for ANR, it has to decode SSB to get the PCI, 5G NR has PCI range 0 to 1007 and PBCH-MIB to know the time and frequency domain information for SIB#1 which carries NCGI information. NR-CGI is combination of PLMN and Cell Identity.
ANR Implementation Approaches
Measurement Report Triggered ANR
When the UE reports Measurement report with PCI information and the serving gNB is unable to find it in the Neighbor Relation table. The Serving gNodeB instruct the UE to retrieve the CGI information of the target cell. Possibly, the UE also needs to be configured with a measurement gap or DRX. The UE detects and decodes also the RMSI (System Information Block#1) from the target cell in order to retrieve the CGI.
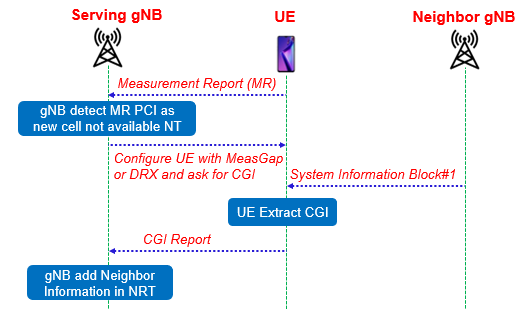
The retrieved CGI is stored and reported to the serving gNodeB. From the reported CGI, the serving gNodeB can extract the gNodeB ID, which is a part of the CGI and other information to update the NRT.
Radio Link Failure Based ANR
This ANR approach is to rely on radio link reestablishment procedures, where the UE provides a new serving gNodeB with information about its previous serving gNodeB, e.g. CGI and PCI. The UE can have obtained the identity information by detecting transmitted identities from its previous gNodeB or the gNodeB can signal the CGI to the UE.
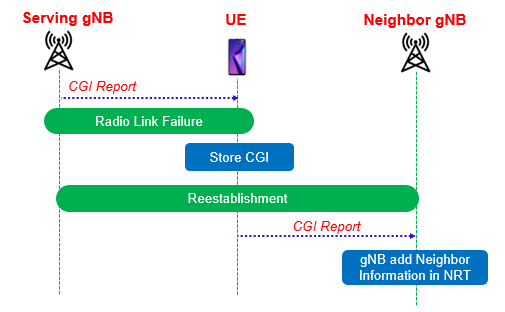
If it can be acceptable to fail to retain a connection due to a missing base station relation, then the RLF reports could enable an efficient mechanism for gNodeB relations establishment. This approach should be able to establish the relation after a single failure.
Retrieval Identity and Transport Address
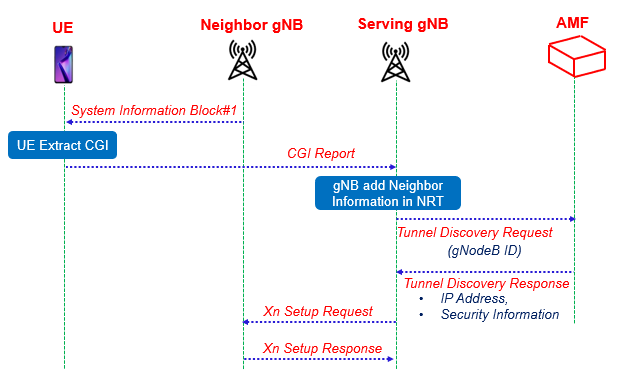
Once a serving gNodeB has obtained the identities related to neighboring gNodeB, it needs to uniquely identify the gNodeB and establish the Xn connection. Then it needs to retrieve neighbor gNodeB transport network layer address i.e. IP address, security information etc. This IP address related information in 5G can be retrieved by gNodeBs via the AMF based on the extracted gNodeB ID from CGI report.
References
- Automatic Neighbor Relations (ANR) in 3GPP NR
- 3GPP TS 28.313 – Self-Organizing Networks (SON) for 5G networks version 16.0.0
- 3GPP TS 38 300- 5G NR Overall description Stage-2
- 3GPP TS 38.401 – 5G NG-RAN Architecture Description
- 3GPP TS 38.412 – 5G NG-RAN NG signaling transport
Related Post
- 5G NR Cell Global Identity (NCGI) Planning and Calculations
- 5G NR Network Relationship – Neighbor Planning
- 4G/5G Great SON – Self Organizing Networks ?
- 5G NR Physical Cell ID (PCI) Planning
- 5G NR Measurement – Serving Cell and Neighbor Cell
- 5G NR Measurement Events