5G NR RRC Procedure and Its States
The Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol is used in on the Air Interface. The major functions of the RRC protocol include connection establishment and release functions, broadcast of system information, radio bearer establishment, reconfiguration and release, RRC connection mobility procedures, paging notification and release and outer loop power control.By means of the signaling functions, the RRC configures the user and control planes according to the network status and allows for Radio Resource Management strategies to be implemented.
The RRC Services and Functions
The main services and functions of the RRC sublayer include:
- Broadcast of System Information related to AS and NAS
- Paging initiated by 5GC or NG-RAN
- Establishment, maintenance, and release of an RRC connection between the UE and NG-RAN including
- Addition, modification, and release of carrier aggregation
- Addition, modification, and release of Dual Connectivity in NR or between E-UTRA and NR.
- Security functions including key management
- Establishment, configuration, maintenance, and release of Signalling Radio Bearers (SRBs) and Data Radio Bearers (DRBs);
- Mobility functions including:
- Handover and context transfer
- UE cell selection and reselection and control of cell selection and reselection
- Inter-RAT mobility
- QoS management functions
- UE measurement reporting and control of the reporting
- Detection of and recovery from radio link failure
- NAS message transfer to/from NAS from/to UE.
What is RRC State?
The operation of the RRC is guided by a state machine which defines certain specific states that a UE may be present in. The different RRC states in this state machine have different amounts of radio resources associated with them and these are the resources that the UE may use when it is present in a given specific state.
The RRC States in 5G New Radio (5GNR)
Appart form RRC connected and RRC IDLE state, 5G NR has introduced a new RRC state names as RRC Inactive state.
- NR-RRC CONNECTED
- NR-RRC INACTIVE
- NR-RRC IDLE
When UE is power up it is in Disconnected mode/Idle mode, It can move RRC connected with initial attach or with connection establishment. If there is no activity from UE for a short time, It can suspend its session by moving to RRC Inactive and can resume its session moving to RRC connected mode.
A UE can move to RRC Idle mode from RRC connected or RRC Inactive state.
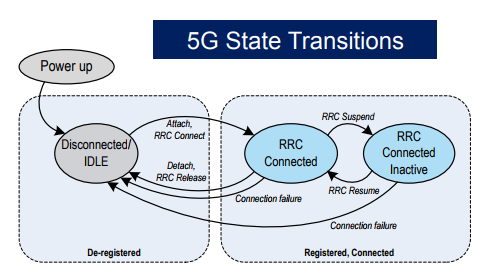
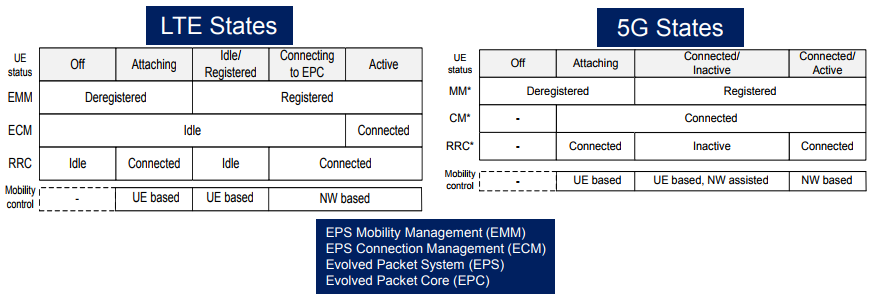
Image Source: Nokia Presentation
RRC Idle Mode Operations:
- PLMN selection
- Broadcast of system information
- Cell re-selection mobility
- Paging for mobile terminated data is initiated by 5GC
- Paging for mobile terminated data area is managed by 5GC
- DRX for CN paging configured by NAS
RRC Inactive Mode Operation:
- Broadcast of system information
- Cell re-selection mobility
- Paging is initiated by NG-RAN (RAN paging)
- RAN-based notification area (RNA) is managed by NG- RAN
- DRX for RAN paging configured by NG-RAN
- 5GC – NG-RAN connection (both C/U-planes) is established for UE
- The UE AS context is stored in NG-RAN and the UE
- NG-RAN knows the RNA which the UE belongs to
RRC Connected Mode Operation:
- 5GC – NG-RAN connection (both C/U-planes) is established for UE
- The UE AS context is stored in NG-RAN and the UE
- NG-RAN knows the cell which the UE belongs to
- Transfer of unicast data to/from the UE
- Network controlled mobility including measurements
Why a new RRC state model required in 5G NR
The RRC States is a solution to the system access, power saving, and mobility optimization. 5G has to support eMBB, URLLC, and Massive IoT services at same cost and energy dissipation per day per area.
5G system access and requested services have different characteristics => Control of connectivity for future services need to flexible and programmable. To meet these different services characteristics it requires new RRC state model.
- To support URLLC services which transmits small packets that require ultra-low latency and/or high reliability
- Massive IoT Devices wakes up seldom power saving mode to transmit and receive a small payload.
- Devices need to camp in low activity state, and sporadically transmits UL data and/or status reports with small payload to the network.
- Devices need periodic and/or sporadic DL small packet transmission.
- When UE is in the connected state, and sporadically transmit UL data and/or status reports with small payload to the network.
- Smartphones and consumer devices which eMBB UE have periodic and/or sporadic UL and/or DL small packet transmission and extreme data rates.
