5G CMAS – Commercial Mobile Alert Service
CMAS-Commercial Mobile Alert Service
3GPP introduced features like CMAS and ETWS as Public Warning System (PWS) services using cell broadcast capabilities. CMAS and ETWS effectively can provide text based alerts and warnings to the public via a broadcast message sent to an alerting area defined by cell site coverage. Cellular devices with in that area will receive and display the alert to the user if those devices are enabled to receive warning messages.
CMAS Key Point
- CMAS is a Public Warning System (PWS) service , widely used in USA and Canada
- It is also know as Wireless Emergency Alert (WEA) service
- CMAS uses Cell Broadcast technique instead point to point
- CMAS alerts use of NR SIB8 RRC message OTA to send alert message to UE
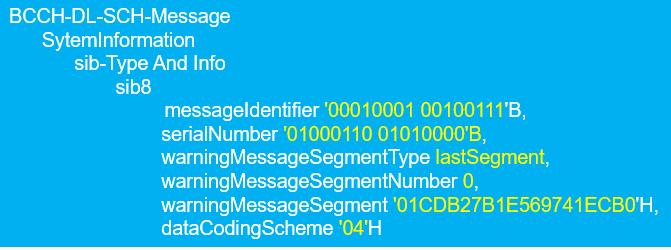
- CMAS message support multiple language depending on the country and UE can get to known language information with the SIB8 IE dataCodingScheme, e.g. 01H value is for English Langauge and 04H value for Spanish
- CMAS alerts can be sent either for whole network or within certain geographical areas, down to the size of a single cell
- CMAS alerts are repeated broadcasted by the network at periodic intervals to ensure that all devices in the area receives the alert
- CMAS alerts are labelled with Serial numbers to allow cellular phones to keep track of which messages broadcast by the network have been displayed already on the device screan, and which are new messages requiring display.
- 3GPP TS 23.041 specification provides all the detailed information for Cell Broadcast Service
- User device can receive the CMAS alerts in both RRC_Connected and RRC_IDLE state
- ETWS is another PWS service used Japan for Earthquake and Tsunami
CMAS Network Architecture
Following figure show the network architecture for Cell Broadcast Services including the CMAS. 5G NR allow to use both reference based and service based architecture.
- Namf: Service-based interface exhibited by AMF
- N50: Reference point between the AMF and the CBCF or between the AMF and the PWS
- SBc: Reference point between the PWS-IWF and the CBC
- N2: Reference point between the NG-RAN and the AMF
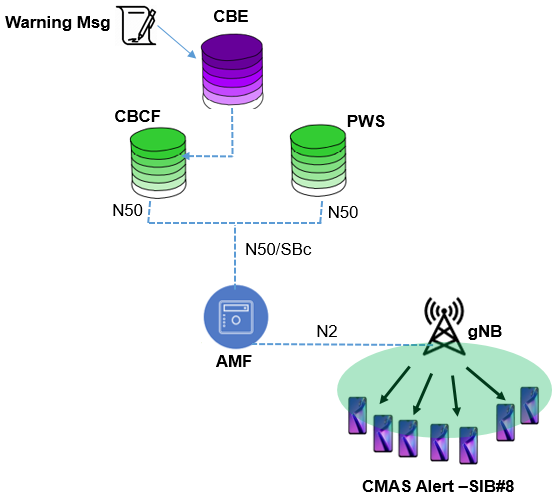
- Cell Broadcast Entity (CBE): The network node is outside of the scope of 3GPP specifications. CBE is responsible for all aspects of formatting alerts messages, including the splitting of a CBS message into a number of pages
- Cell Broadcast Center Function (CBCF) : 3GPP has defined CBCF as a network function with 5G Core. The CBCF may be connected to several several CBEs and AMFs and responsible for following.
- allocation of serial numbers for alerts messages
- determining the set of cells to which a CMAS message should be broadcast
- determining the time and period at which a CMAS message should cease being broadcast
CMAS Call Flow in 5G NR
Following figure show the CMAS E2E call flow including different network functions.
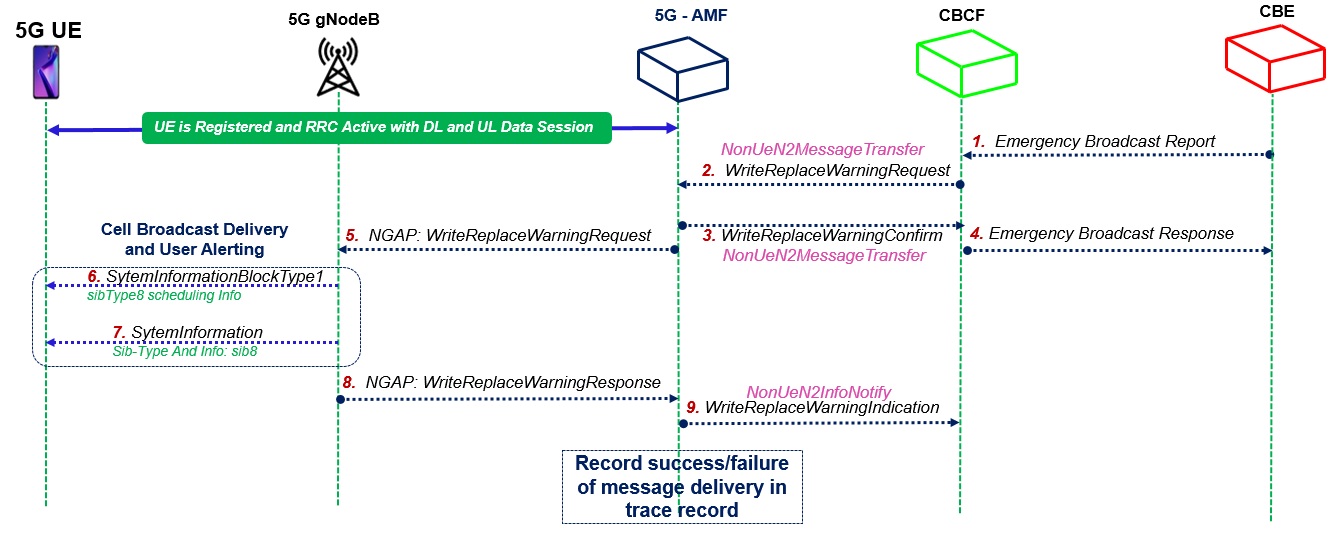
Call Flow Message Sequence
- Step#1 Emergency Broadcast Report: CBE entiry prepares the Emergency broadcast report as per information Source such as PSAP or Regulator e.g. “warning type”, “warning message”, “impacted area”, “time period”.
- Step#2 Non-UeN2MessageTransfer (Write-Replace Warning Request) : The CBCF sends a WriteReplaceWarningRequest message to AMF containing the warning message to be broadcast and the delivery attributes like Message Identifier, Serial Number, Tracking Area ID list, Warning Area, CWM Indicator, Send Write-Replace-Warning-Indication, Global RAN Node ID to AMFs. CBCF selects the AMFs based on the impacted area mapping.
- Step#3 Non-UeN2MessageTransfer (WriteReplaceWarningConfirm): The AMF sends a WriteReplaceWarningConfirm message o the CBCF indicating that the AMF has started to distribute the warning message to gNodeBs nodes.
- Step#4 Emergency Broadcast Response: Upon reception of the WriteReplaceWarningConfirm messages from the AMFs, the CBCF may confirm to the CBE that it has started to distribute the warning message using the Emergency Broadcast Response.
- Step#5 WireReplaceWarningRequest: The AMF forwards WriteReplaceWarningRequest to gNBs. The AMF shall use the Tracking Area ID list to determine the gNB in the delivery area. If the Tracking Area ID list is not included and no Global gNB ID has been received from the CBCF, the message is forwarded to all gNBs connected to the AMF. If a Global gNB ID has been received from the CBCF, the AMF shall forward the message only to the gNB indicated.

- Step#6 SystemInfromationBlockType1: Upon recieving WriteReplaceWarningRequest message from AMF, gNB identify the cells and broadcast the updated SIB#1 including the SIB#8 scheduling information. UE needs to decoded the updated SIB1
- Step#7 SystemInformation: The system information includes SIB8 information having the CMAS alert message
- Step#8 WireReplaceWarningResponse: gNBs sends WriteReplaceWarning Response messages to AMF and the AMF determines the success or failure of the delivery and creates a trace record.

- Step#9 NonUeN2InfoNotify (Write-Replace Warning Indication): AMF notify the CBCF nodes with Write-Replace Warning Indication. This message exchange is optional.
CMAS UE Signalling for Idle and Connected Mode
Following figure show the RRC signalling for UE in RRC_IDLE ,RRC_INACTIVE and RRC_CONNECTED.
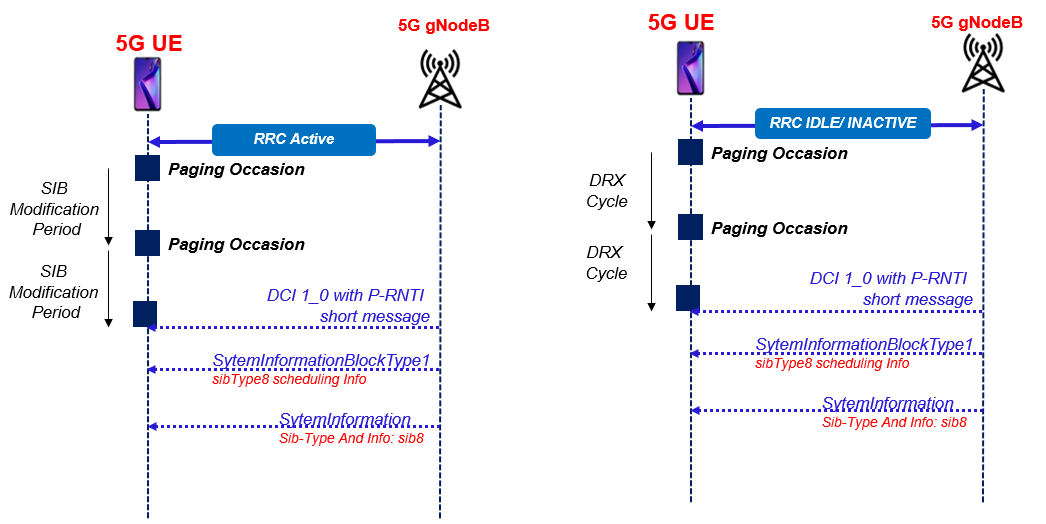
- UE in RRC_CONNECTED
- UE in RRC_Connected monitor the DCI 1_0 once per System Information Modification Period during any Paging Occasion and assuming the UE has been configured with a Common Search Space to monitor paging within the active Bandwidth Part. DCI 1_0 includes a ‘Short Message’ scrambled using the P-RNTI. This ‘Short Message’ can be used to indicate that System Information has been updated and needs to be re-acquired or there is an incoming CMAS message
- UE in RRC_IDLE and RRC_INACTIVE
- When UE in RRC_IDLE or RRC_INACTIVE monitor the PDCCH DCI 1_0 once per DRX cycle during the UE’s Paging Occasion.
References
- 3GPP TS 23.041 Technical realization of Cell Broadcast Service (CBS)
Related Posts