What is an xApp – ORAN Automation
Introduction
Service Providers (MNOs) are facing strong pressures to evolve their operations and business to support sustainable growth. Extensive demand for mobile bandwidth is all time high, while ARPUs have been flat and declining. On top of this, mobile networks becoming more complex resulting cost extensive operations. Supporting different access networks like 2G, 4G and now 5G, requires even more RAN capacity and denser networks. With increased data rates and ultra-reliable lower latency requirements the network densification will be a critical part of deploying 5G architecture.
The technology evolved provided Open RAN as solution for above problem by disrupting traditional closed and proprietary RAN solutions by offering true hardware and software disaggregation which helps service providers reduce deployment cost and complexity.
What is an xApp ?
xApp (eXtended application) is a software application used by RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) to implement specific functions or services in near-real time within the O-RAN architecture. These applications or services includes function like radio resource management, mobility management, and security. xApp are typically deployed on top of the Radio Intelligent Controller (RIC) and communicates with other components over E2 interface within the O-RAN architecture.
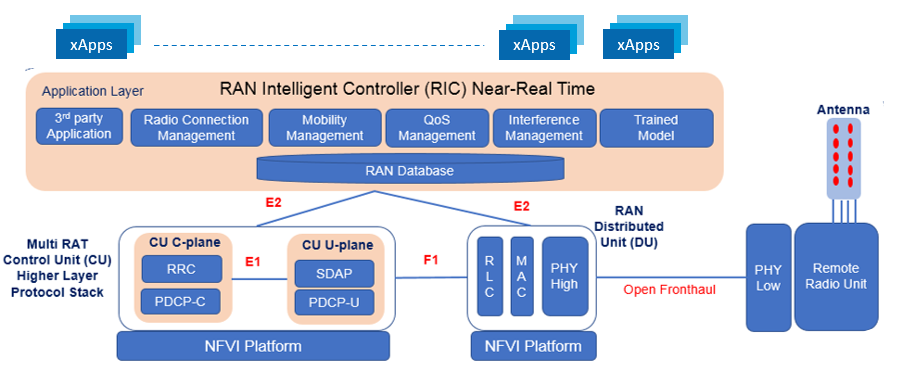
Key Pointers
- xApps supports cloud-native microservice based deployment
- xApps are host on Near-RT RAN Intelligent Controller usually at networks edge
- xApps are responsible for controlling and optimizing RAN functions and enhance the spectrum efficiency
- xApps provides “northbound” interfaces A1 and O1 interfaces toward the Non-RT RIC
- xApps collects data from RAN functions (CUs,DUs) on “southbound” interface as E2 Interface
- xApps also have an internal messaging framework to handle conflict mitigation, subscription management, app lifecycle management functions and security
xApps Category
- Radio resource management: xApps can be used to optimize the use of radio resources in the O-RAN architecture, such as by allocating frequency bands or scheduling transmissions.
- Mobility management: xApps can be used to manage the movement of devices within the O-RAN architecture, such as by providing handover support or tracking device location.
- Quality of Service (QoS): xApps can be used to implement QoS control functions, such as traffic management or congestion control, to optimize the performance of the O-RAN architecture.
- Security: xApps can be used to implement security functions, such as authentication and encryption, to protect the O-RAN architecture from threats.
How xApps Evolved ?
The SDN approach that Open RAN brings to communications networks centralizes network intelligence in a network element by separating User Plane (UP) and Control Plane (CP) functions. With the tradition RAN vendors control plane the set of control algorithms in the RAN protocol stack has been closed and vendor proprietary. These control algorithms, that range from RRC functions like admission control, mobility control, etc. to MAC functions like PRB allocation, beamforming control, etc., directly impact how efficiently the RAN uses an operator’s valuable spectrum assets and what quality of service (QoS) operators can deliver to their subscribers.

With the mature open RAN, O-RAN Alliance has taken a software-defined approach and made it possible for external developers to program the near-real-time RAN control plane, i.e., the subset of control algorithms that can tolerate control loop delays of 10 milliseconds to 1 second. The key element in the O-RAN architecture that makes this possible is the Near-Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller or Near-RT RIC. The application that are developed by programmers to control algorithms are referred as xApps.
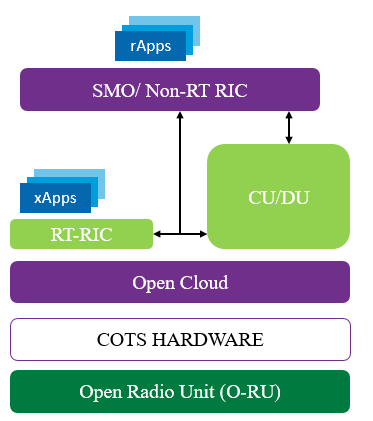
Does SON and xApps same ?
SON is Self Organizing Networks, in our point of view xApps functions are similar and can be augment as the next generation of SON for Open RAN. xApps are repackage SON to provide a flexible, standards based, interoperable, multivendor, programmable feature applications for RAN optimization.
xApps Vendor Ecosystem
- Accelleran: Belgian start-up Accelleran has released their own cloud-native Open RAN software, known as dRAX. Its dRAX-RIC near real-time platform enables the roll-out of smart apps for managing and optimizing the RAN. It has been developed as an open platform to allow third-party app integration and benefits of AI and Big Data to enable near-real time control functions. Its own library of xApps available for automated installation and support third party xApps as well . Its xApp offerings include:
- dRAX Dashboard
- Near zero-touch provisioning
- Automated Neighbour Manager
- Smart Handover
- Automated PCI Allocation
- Airhop: Airhop is a cloud native radio access network software technology company. It has joined the Open Networking Foundation (ONF), an organization that launched the SD-RAN project in 2020 to develop elements to be used in disaggregated RAN rollouts. Since joining the ONF, Airhop has been developing a near-RT RIC and set of xApps for controlling the RAN.
- Rakuten Symphony : Another key player in the RIC space is Rakuten Symphony, a provider of open vRAN technology. Rakuten Symphony has already developed its own gNB with virtual Centralised Unit (vCU), gNB virtual Distributed Unit (vDU), and integrated 3rd party O-RAN compliant Radios. More recently, Rakuten Symphony has been developing its own near-RT RIC platform as well as its own xApps.
- Juniper Networks: Juniper Networks in partnership with Turk Telekom has entered the Open RAN space with its newly developed RIC. Its RIC comes in both near-RT and non-RT forms, with the ability to host both xApps and rApps from any third-party providers.
- Mavenir: In partnership with Airtel, Mavenir demonstrated its O-RAN RIC at the Global O-RAN Alliance Plugfest in India towards the end of 2020. During the event the partners successfully demonstrated the ability to optimise configuration parameters and improve on pre-defined KPIs.
- Nokia: Nokia announced the launch of its Service Enablement Platform (SEP) in March 2021. Its commercial solution will deliver network programmability and introduce AI/ML into the Open RAN ecosystem. Nokia’s SEP launched with a selection of xApps, including Advanced Traffic Steering and Anomaly Detection. Nokia trialled a number of xApps in partnership with AT&T.
- Parallel Wireless: Parallel Wireless have also developed its own OpenRAN Controller to enable Open RAN solutions. Its controller is the first to provide an “all G” RAN, offering virtualised 2G BSC, 3G RNC, 4G eNB, X2/S1 Gateway in any combination.
- Sterlite Technologies (STL): At the Global O-RAN Alliance Plugfest hosted in India in 2020, hosted by Bharti Airtel, STL and ASOCS showcased the fruits of the partnership: its RAN Intelligent Controller. The demonstration highlighted the near-RT RIC’s mobility load balancing capabilities on the O-RAN E2 interface, with future prospects to handle and balance increasing network loads through software defined networks.
References
- VMware RIC
- Why the RAN Intelligent Controller is the Brain of Open RAN
- RIC, xApps, rApps: Who are the key players?
Related Posts
- O1 Interface in Open RAN
- E2 Interface in Open RAN
- Open RAN (O-RAN) Reference Architecture
- 5G RIC – RAN Intelligent Controller
- Cloud RAN Orchestration and Management
