5G SLIV – Start and Length Indicator Value
Introduction
In 5G NR, SLIV means Start and Length Indicator Value. It is used for Time domain resource allocation for PDSCH and PUSCH. In SLIV, the letter ‘S’ defines the start symbol and ‘L’ define the no. of consecutive symbols for the time domain resource allocation.
SLIV is a single encoded value and represent two value i.e. start symbol and no. of symbols can be derived using the equation mention later in this post.
Key pointers
- SLIV, the letter ‘S’ defines the start symbol and ‘L’ define the no. of consecutive symbols
- In SLIV, starting Symbol and Length is always configured such that the resource allocation remains within the boundaries of a specific slot and does not overlap into the next slot
- It is an encoded single value as per 3GPP 38.214
- It minimum value can be 0 and maximum value can be 104
- The SLIV coding has been designed to minimize the no. of bits required to signal it
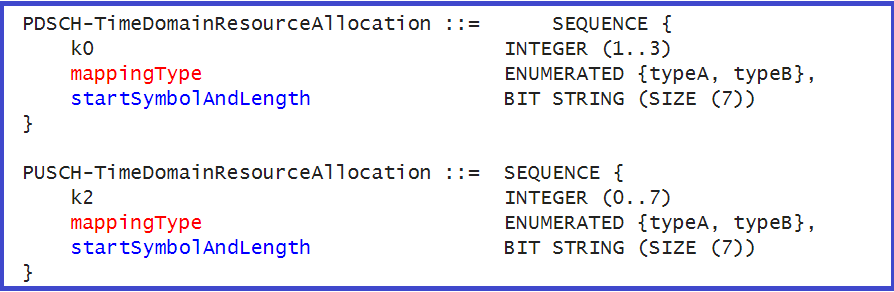
- SLIV is indicated in RRC PDSCH or PUSCH TimeDomainResourceAllocationstart IE with parameter SymbolAndLength and represented with 7 bits string
Why do we need SLIV in 5G?
In legacy 4G LTE, scheduling in time domain was done at subframe level where as in 5G NR, it is at slot and symbol level with slot. so to support this SLIV is introduced in 5G NR. It also optimize the transmission of data over the air interface in 5G networks by reducing the overhead associated with transmitting control information.
5G SLIV IEs for PDSCH and PUSCH
Following figure the SLIV IEs i.e. startSymbolAndLengh send in the RRC message for common and dedicate signaling.
SLIV Calculation Formula
3GPP 38.214 specification has given following formula to calculated and decode the SLIV. It take two inputs S – Start Symbol Index and L – N0. of Consecutive Symbols, where 0 < L <= 14 – S
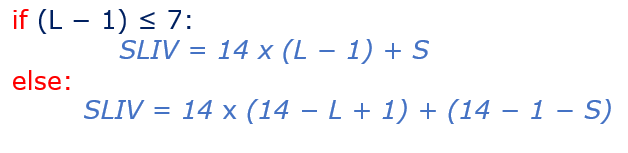
Calculation Example
- Example#1 – Lets assume, we are using PDSCH mapping type A, where L = 8 and S = 2, then using above formula SLIV can be calculated as:
- L-1 = 8-1 = 7 <= 7 , which is true, so we need to use first part of equation i.e. if part .
- SLIV = 14 x (L – 1 ) +S
- = 14 x (8 – 1 ) + 3
- = 14 x 7 + 3
- = 98 + 3 =101
- L-1 = 8-1 = 7 <= 7 , which is true, so we need to use first part of equation i.e. if part .
- Example#2 – where L = 11 and S = 3, then using above formula SLIV can be calculated as:
- L-1 = 11-1 = 8 < 7 which is false statement so we need to use second part of equation i.e. else part
- SLIV = 14 x (14 – L + 1 ) + (14 -1 – S )
- = 14 x (14 – 11 + 1) + (14 – 1 – 3)
- = 14 x 4 + 10
- = 56 + 10 = 66
- L-1 = 11-1 = 8 < 7 which is false statement so we need to use second part of equation i.e. else part
Valid S and L combinations
With the above equation we can have many possible value of SLIV, but as per 38.214 specification only following valid S and L combination are allowed for PDSCH (Fig#1) and PUSCH (Fig#2)
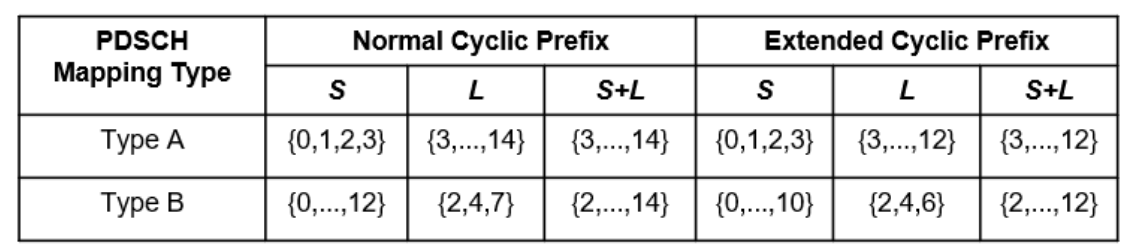
Fig#1: Valid S and L combinations for PDSCH

Fig#2 Valid S and L combinations for PUSCH
SLIV Mapping Table for PDSCH and PUSCH
Below figure show the mapping table of SLIV for PDSCH and PUSCH derived using the above formula. Vertical plane show the start symbol and Horizontal plane shows the respective possible Length.
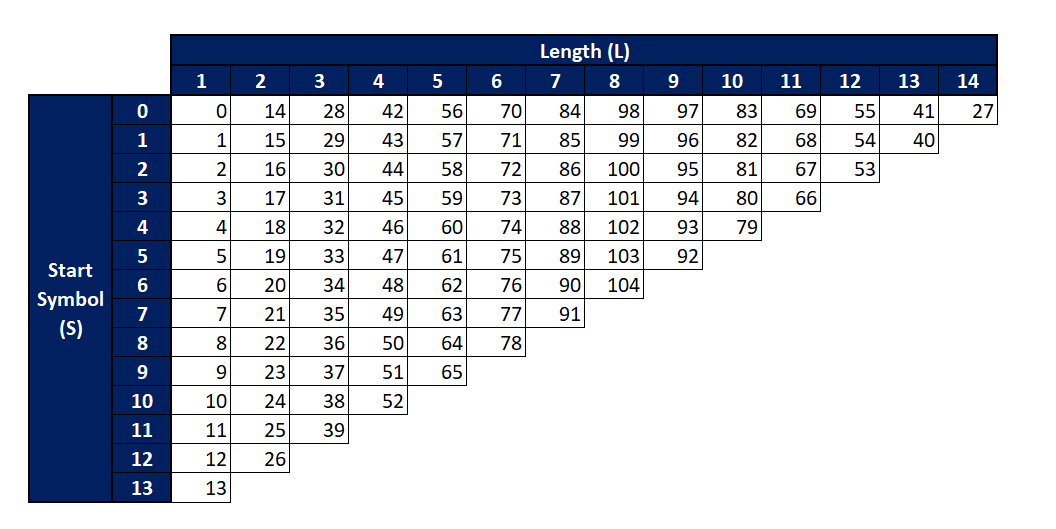
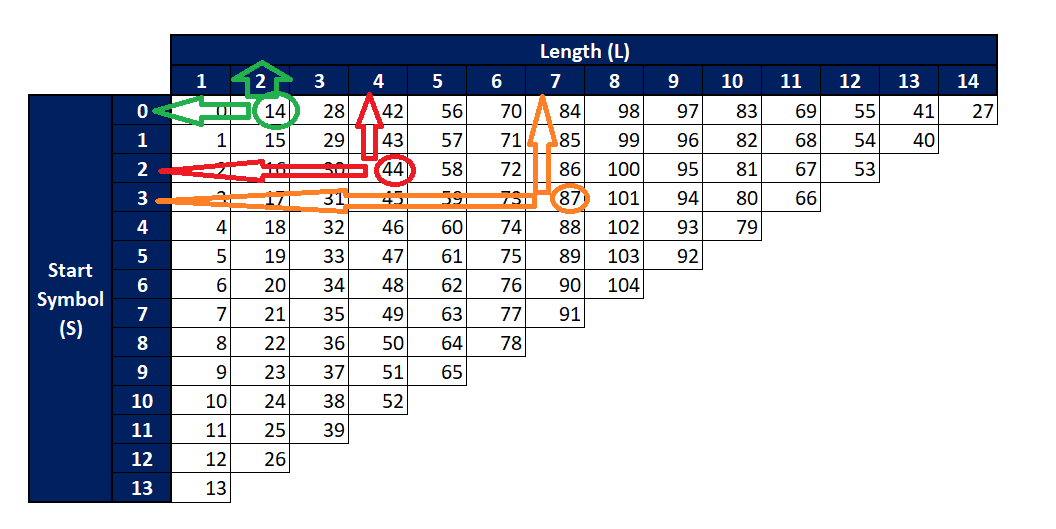
How to use above mapping table for 5G SLIV
Let’s take following log snippet to know how to use above table.

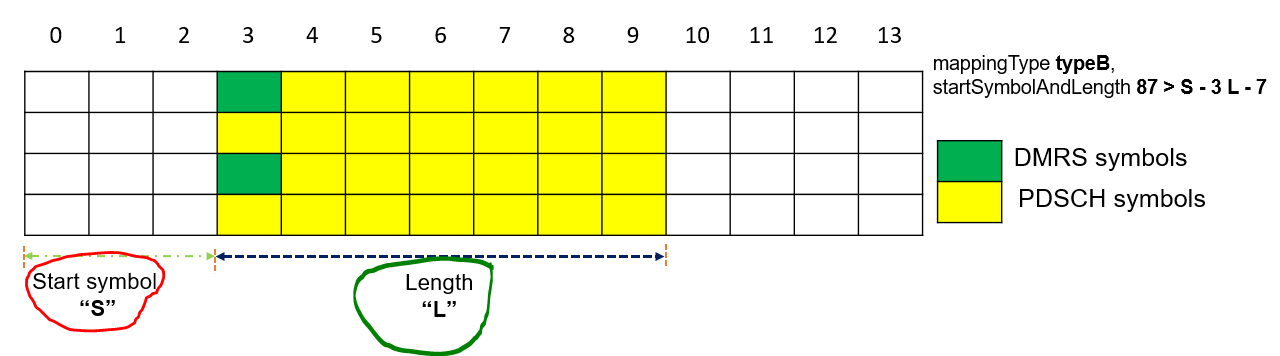
1st part says, the PDSCH mapping type B with StartSymbolAndLength 14. If we look-up 14 with in SLIV mapping table, it maps start symbol as 0 and length as 2.
Similarly, for
- startSymbolAndLength 44 —> S = 2 and L =4
- startSymbolAndLength 87 —> S = 3 and L = 7
Author

References
Related Posts
- 5G NR Quasi-Colocation Concept, Types and Application
- 5G NR Reference Signals (DMRS, PTRS, SRS and CSI-RS)
- 5G NR Sounding Reference Signal (NR-SRS)
- 5G NR SSB Positioning – Time and Frequency Resources
- PDSCH mapping – type A and type B