3GPP NTN Use Case Categories: Service Continuity, Ubiquity, Scalability
Introduction
As per 3GPP TR 22.822, based on the analysis of satellite network characteristics and their integration with 5G systems, it defines three primary categories of use cases for Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN). These categories provide a structured way to understand how satellite networks complement terrestrial deployments and address their inherent limitations.
Important point to note that these categories are not mutually exclusive. A single use case may span one, two, or even all three categories depending on the service requirements, user mobility, and operational environment. The three categories are:
- Service Continuity
- Service Ubiquity
- Service Scalability
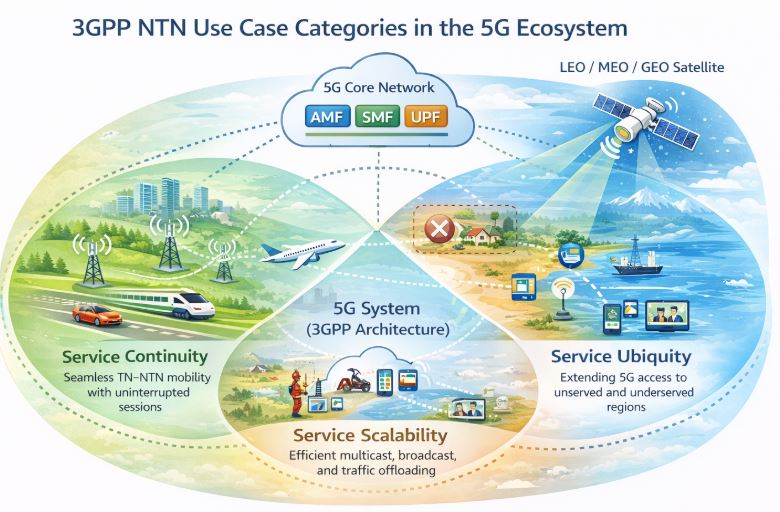
Each category highlights a distinct architectural and operational benefit offered by NTN within the 5G ecosystem.
NTN Service Continuity: Seamless Access Across Networks
Terrestrial network deployments are typically optimized around dense population and economic viability, rather than geographical blanket coverage. As a result, there are many areas—such as highways, rural regions, oceans, and airspace—where continuous terrestrial 5G coverage cannot be guaranteed.
User Equipment (UE), whether carried by pedestrians or mounted on moving platforms, may frequently traverse these coverage gaps. Typical examples include:
- Land-based platforms: cars, buses, trucks, trains
- Airborne platforms: commercial and private aircraft
- Maritime platforms: ships and offshore vessels
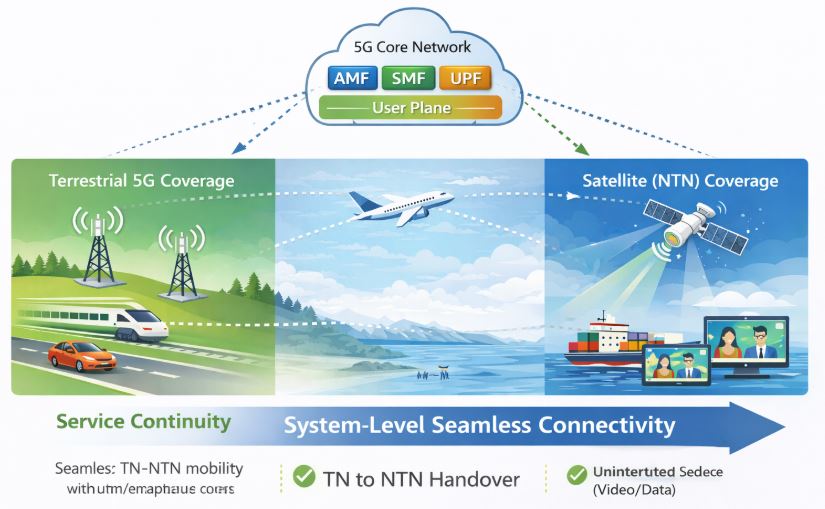
During such journeys, relying solely on terrestrial networks may lead to service interruptions, dropped sessions, or degraded user experience.
Role of NTN in Service Continuity
Use cases under the Service Continuity category address this limitation by enabling continuous access to 5G services as UEs move between terrestrial and satellite networks. The objective is not only coverage extension, but to provide seamless service across heterogeneous access networks. NTN access networks allow:
- Session continuity when terrestrial coverage is unavailable
- Support for long-distance and high-mobility scenarios
- Connectivity for fleets of UEs, whether geographically dispersed or locally clustered
From an architectural perspective, this continuity is achieved by integrating NTN into the 5G system so that UEs can transition between terrestrial and non-terrestrial network (NTN) access with minimal service disruption.
NTN Service Ubiquity: Service to Unserved and Underserved
Why Ubiquitous Coverage Is Needed
There are territories, where terrestrial networks are either not deployed or temporarily unavailable. It could be because of:
- Financial constraints, where expected infrastructure ROI does not justify
- Natural disasters e.g. earthquakes, floods, or storms, which may partially or completely destroy terrestrial network infrastructure
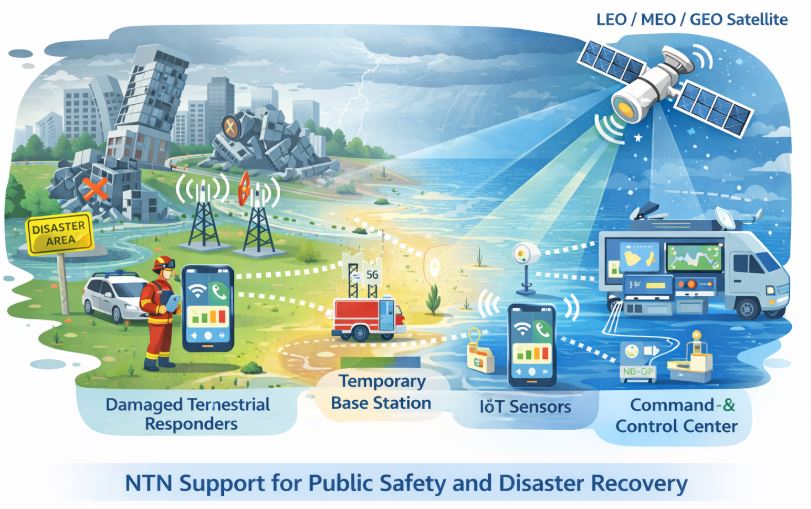
Users located in these areas could not use 5G services, unless an alternative access mechanism is available.
NTN as an Service Ubiquity Enabler
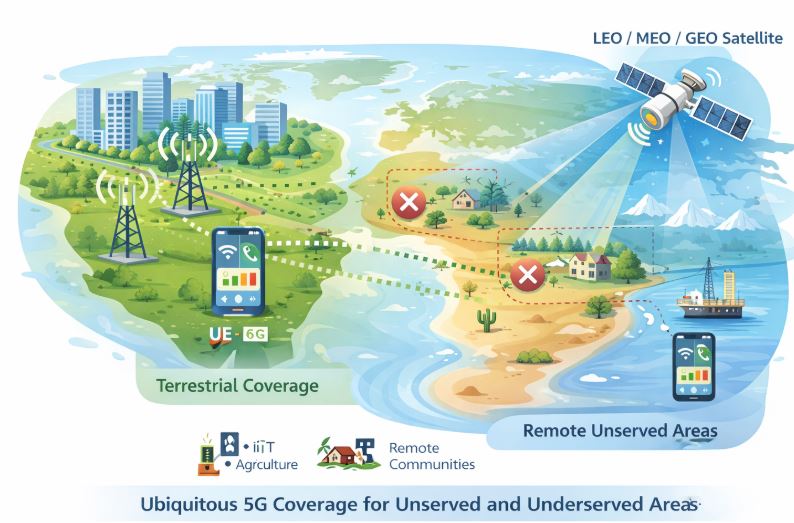
The Service Ubiquity category focuses on enabling 5G access in areas that are not served or underserved by terrestrial networks. NTN-based 5G access networks play a critical role in ensuring that connectivity is not limited by geography, infrastructure availability, or short-term disruptions. Typical use cases include:
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications, such as: Smart agriculture
- Critical infrastructure monitoring and control (e.g. pipelines)
- Asset tracking and tracing
- Public safety and emergency communications, especially during disaster recovery operations
- Residential or home broadband access in remote or sparsely populated regions
By leveraging NTN, these services can be delivered without relying on dense terrestrial infrastructure, ensuring that connectivity remains available when and where it is most needed.
NTN Service Scalability: Efficient Distribution of Content
Compared to terrestrial networks, satellite systems inherently cover extremely large geographical areas, often equivalent to tens of thousands of terrestrial cells. This characteristic makes satellite networks particularly well suited for multicast and broadcast services.
Rather than duplicating the same content across many terrestrial base stations, satellites can efficiently distribute identical data streams over wide regions, and in some cases, directly to user equipment.
Scalable Content Distribution and Traffic Offloading
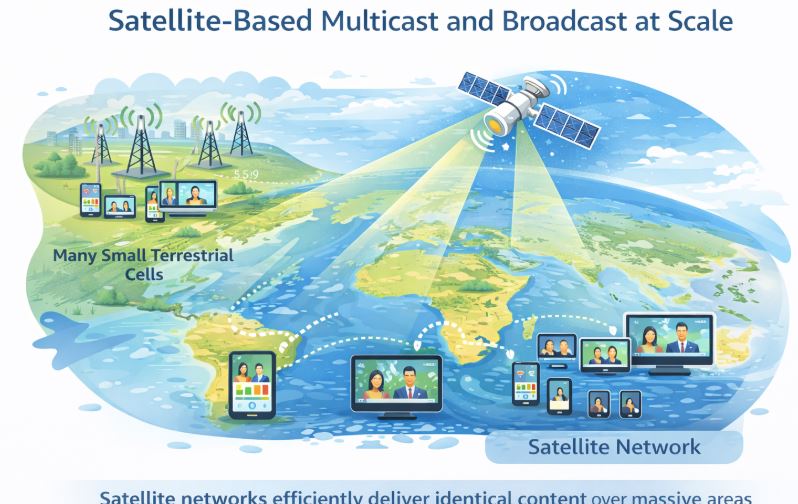
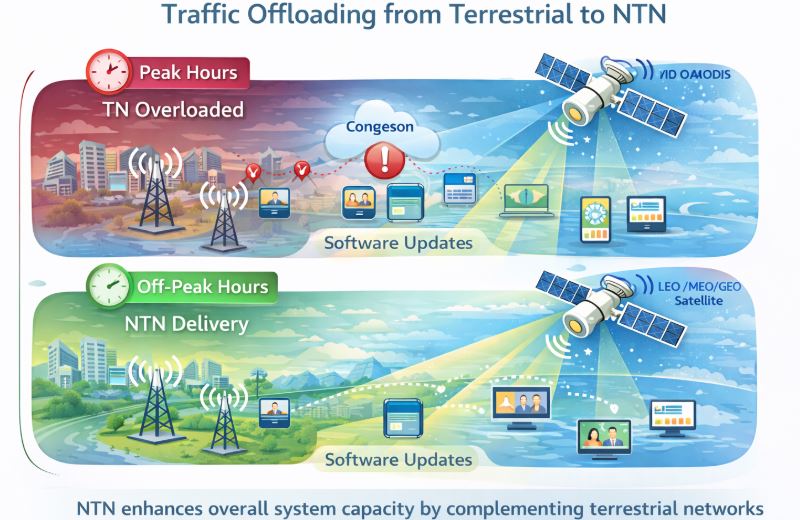
Use cases under the Service Scalability category exploit this capability to:
- Broadcast or multicast non-time-sensitive data
- Offload traffic from terrestrial networks during peak hours
- Deliver high-bandwidth content efficiently
A prominent example is the distribution of rich and very rich media content, such as: Ultra High Definition (UHD) video and Advanced media formats (e.g. 3D or immersive content). NTN networks can transmit such content during non-busy hours, reducing congestion on terrestrial networks while ensuring timely availability for end users.
Conclusion
The three 3GPP-defined NTN use case categories—Service Continuity, Service Ubiquity, and Service Scalability—collectively illustrate how satellite networks enhance and extend the capabilities of terrestrial 5G systems.
By enabling seamless mobility, universal access, and efficient large-scale content delivery, NTN transforms satellite connectivity from a niche solution into a core component of future mobile networks. As 5G continues to evolve and 6G concepts emerge, these categories will remain fundamental in shaping truly global, resilient, and scalable communication infrastructures.
References
- 3GPP TR 38.811 : Study on New Radio (NR) to support non-terrestrial networks
- 3GPP TR 38.821 : Solutions for NR to support non-terrestrial networks (NTN)
- 3GPP TR 23.737 – Study on architecture aspects for using satellite access in 5G
- RP-193234 : Solutions for NR to support non-terrestrial networks (NTN)
- TS 22.261 : Service requirements for the 5G system; Stage 1 (Release 18)
Related Post
- 5G Non-Terrestrial Network Terminologies
- The Future and Opportunities of Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs)
- SpaceX – Starlink System Architecture for Internet
- Direct to Cell Satellites – SpaceX Cell Tower


