What Is NETCONF? Why Do We Need It?
Introduction
NETCONF full-name is Network Configuration Protocol. It is a network management protocol which allow a NMS (Network Management System) to deliver, modify and delete configuration of connected n/w device i.e. router, eNodeB, gNodeB, DU, CU or RU. It is developed and standardized by the IETF and for O-RAN, it is looked after WG4 (Work Group#4).
NETCONF protocol is based on XML (Extensible Markup Language) based data encoding for configuration data and protocol messages. It works on server client concept and use RPC (Remote Procedure Call) mechanism to implement communication between server and client.
The client process runs on NMS which can be a script or an application and the server is a typical network device.
NETCONF Key Pointer
- NETCONF full-name is Network Configuration Protocol
- NETCONF uses a hierarchical protocol framework, make it more suitable for on-demand, automation, and cloud-based networks.
- It is used to deliver, modify and delete configuration to Network Devices
- XML (Extensible Markup Language) is used for data encoding for configuration data and protocol messages
- Works on server client concept, NMS acts as client and Network Device as server
- Uses RPC (Remote Procedure Call) mechanism to implement communication between server and client
- Performs operations based on the YANG model, to reduce network faults caused by manual configuration errors
- NETCONF comes in momentum for network automation requirements
- Provides security mechanisms such as authentication and authorization to ensure message transmission security.
- Provides a transaction mechanism to support data classification, storage, and migration, phase-based submission, configuration isolation,
- Also supports overall configuration delivery, verification, and rollback, minimizing the impact on network services
- Allows vendors to define their own protocol operations, to implement unique management functions
Why we Need NETCONF
New emerging Cloud Network’s on key requirement is Network automation for fast and on-demand service provisioning and automatic Operations & Management. This requirement cannot be met using the traditional available methods like CLI and SNMP have. CLI and SNMP have following limitation which is taken care with NETCONF.
Disadvantages of CLI
- CLI-based configuration is complex
- CLIs varies by vendor, so users have to learn and adapte scripts for each vendor’s CLI
- Frequent changes to the CLI structure and syntax make it difficult to maintain CLI scripts
- The output of commands is structure-agnostic, unpredictable, and prone to changes, causing difficulties in automatically parsing CLI scripts
Disadvantages of SNMP
- SNMP does not support the transaction mechanism, resulting in a low configuration efficiency.
- SNMP uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which cannot provide reliable and ordered data transmission and lacks an effective security mechanism.
- SNMP does not have a mechanism for submitting configuration transactions.
- SNMP manages device configuration on a per-device basis and does not support network-level configuration or multi-device configuration collaboration
How Does NETCONF Work?
A basic NETCONF system contains at least one NMS that manages network-wide devices as shown in following figure. The NETCONF architecture consists of two roles: client and server.
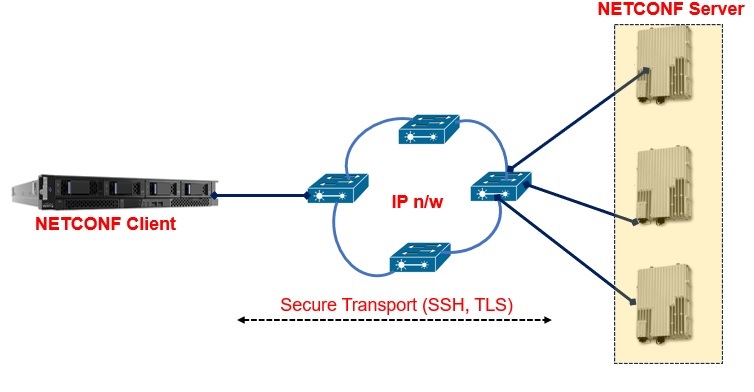
A client provides the following functions:
- Manages network devices using NETCONF.
- Sends RPC requests to a NETCONF server to query or modify one or more parameter values.
- Learns the status of a managed device based on the alarms and events sent by the NETCONF server of the managed device.
A server maintains information about managed devices and responds to the client-initiated requests.
- When receiving a request from a NETCONF client, the NETCONF server parses the request and sends a reply to the client.
- If a fault or another type of event occurs on a managed device, the NETCONF server reports an alarm or event to the client through the notification mechanism. This allows the client to learn the status of the managed device.
Establishing a NETCONF Session
The NETCONF client and server use the RPC mechanism to communicate with each other. The communication is allowed only after a secure and connection-oriented session is established between them. The client sends an RPC request to the server, and the server returns a reply to the client after processing the request.
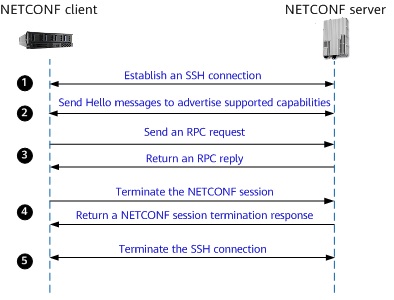
The process of establishing and terminating a NETCONF session is as follows:
- A client establishes an SSH connection with a server, and then establishes a NETCONF session with the server after authentication and authorization are complete.
- The client and server send Hello messages to negotiate capabilities.
- The client sends one or more RPC requests to the server. The following lists some request examples:
- Modify and commit the configuration.
- Query the configuration data or status.
- Perform maintenance operations on the device.
- The client terminates the NETCONF session.
- The SSH connection is terminated.
Protocol Framework for NETCONF
NETCONF protocol framework uses a hierarchical structure. Each layer encapsulates certain functions and provides services for its upper layer. This structure enables each layer to focus only on a single aspect of NETCONF and reduces the dependencies between layers. In this way, the internal implementation changes of one layer have minimum impact on other layers.
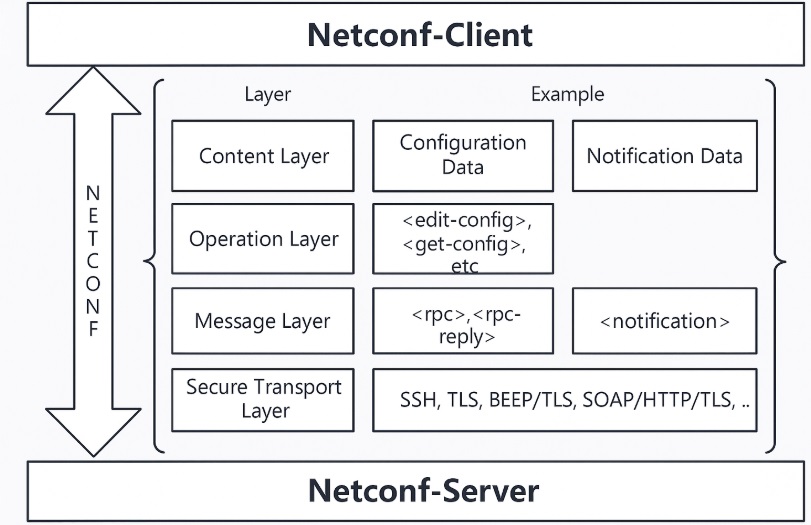
NETCONF can be conceptually partitioned into four layers, which are the Secure Transport, Messages, Operations, and Content layers from bottom to top.
- Secure Transport layer: This layer is responsible for communication between the client and server. NETCONF can be layered over any transport protocol that meets basic requirements e.g SSH, TLS, HTTPs etc. SSH is the preferred transport protocol in NETCONF for transmitting XML information.
- Messages layer: This layer provides framing mechanism for encoding RPCs and notifications which is transport-independent . A client encapsulates an RPC request into an <rpc> element and sends it to a server. The server encapsulates the result of processing this request into an <rpc-reply> element and sends it to the client.
- Operations layer: This layer defines a set of base protocol operations, which are invoked as RPC methods with XML-encoded parameters.
- Content layer: This layer is defined by a data model that manages data. Currently, mainstream data models include Schema and YANG.
- Schema is a set of rules defined to describe XML files. A device uses a Schema file (similar to an SNMP MIB file) to provide device configuration and management interfaces for an NMS.
- YANG is a data modeling language designed for NETCONF. A client can compile RPC operations into XML messages to implement client-server communication in compliance with YANG model restrictions.
NETCONF Message Format
The following figure shows the structure of a complete NETCONF YANG request message

NETCONF Communication Framework
The client-initiated RPC requests and the server-originated replies are both encoded in <rpc> and <rpc-reply> elements using XML. This request-reply framework is independent of transport layer protocols. The following lists some basic RPC elements:
- <rpc> An <rpc> element is used to enclose a request sent from a NETCONF client to a NETCONF server.
- <rpc-reply> An <rpc-reply> element is sent by a NETCONF server in response to each <rpc> request.
- <rpc-error> If any error or alarm occurs during the processing of an <rpc> request, the NETCONF server returns an <rpc-reply> message containing only the <rpc-error> element to the NETCONF client.
- <ok> If no error or alarm occurs during the processing of an <rpc> request, the NETCONF server returns an <rpc-reply> message containing only the <ok> element to the NETCONF client.
NETCONF Configuration Database
A configuration database is a complete set of configuration parameters for a device. NETCONF defines the existence of one or more configuration database and allows configuration operations on them. Only the <running/> configuration database is available in the base model of NETCONF. Additional configuration databases can be defined by capabilities, and are available only on devices that support the capabilities.
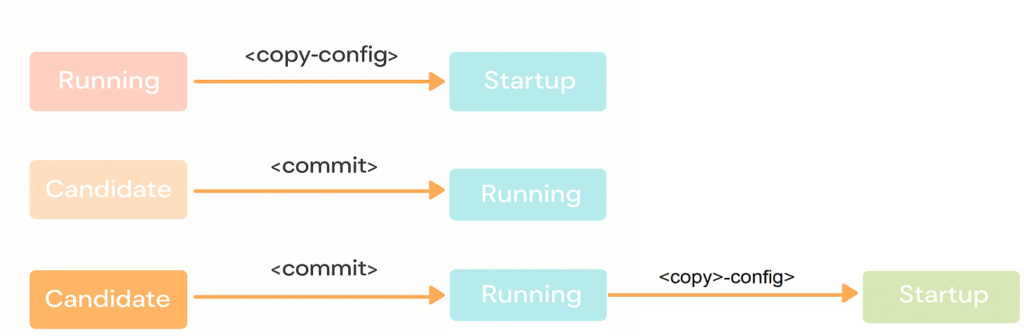
- <running/>: a running configuration database. It stores all configurations that are currently active on a network device. Only one <running/> configuration database exists on a device, and it always exists.
- <candidate/>: a candidate configuration database. It stores configuration data that is about to be committed to <running/> on a device. The <candidate/> configuration database can be manipulated without impacting the device’s current configuration. The <commit> operation is performed to commit the candidate configuration. To support the <candidate/> configuration database, a device must support the candidate configuration capability, which is a standard NETCONF capability.
- <startup/>: a startup configuration database (similar to a saved configuration file). It stores the configuration data to be loaded during device startup. To support the <candidate/> configuration database, a device must support the distinct startup capability, which is a standard NETCONF capability.
NETCONF Operations and Capabilities
NETCONF provides a set of basic operations for managing device configurations and querying device configuration and status data. It also supports additional operations based on the capabilities advertised by a device.
Basic Operations of NETCONF
NETCONF base capability provides a set of operations to modify configurations in datastores and obtain information from datastores. The base capability provides only a small set of low-level operations as given in below table.
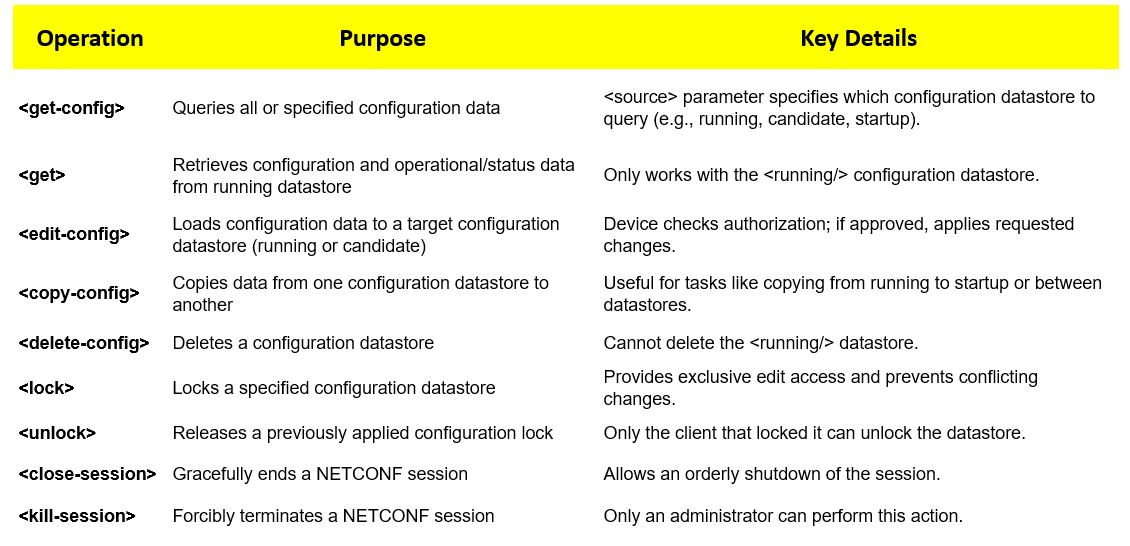
NETCONF Standard Capabilities
NETCONF defines a series of standard capabilities, which enhance the NETCONF functionality and strengthen the fault tolerance and scalability. This facilitates the implementation of the NETCONF-based open network management architecture, and provides an efficient method for vendors to develop new functions.
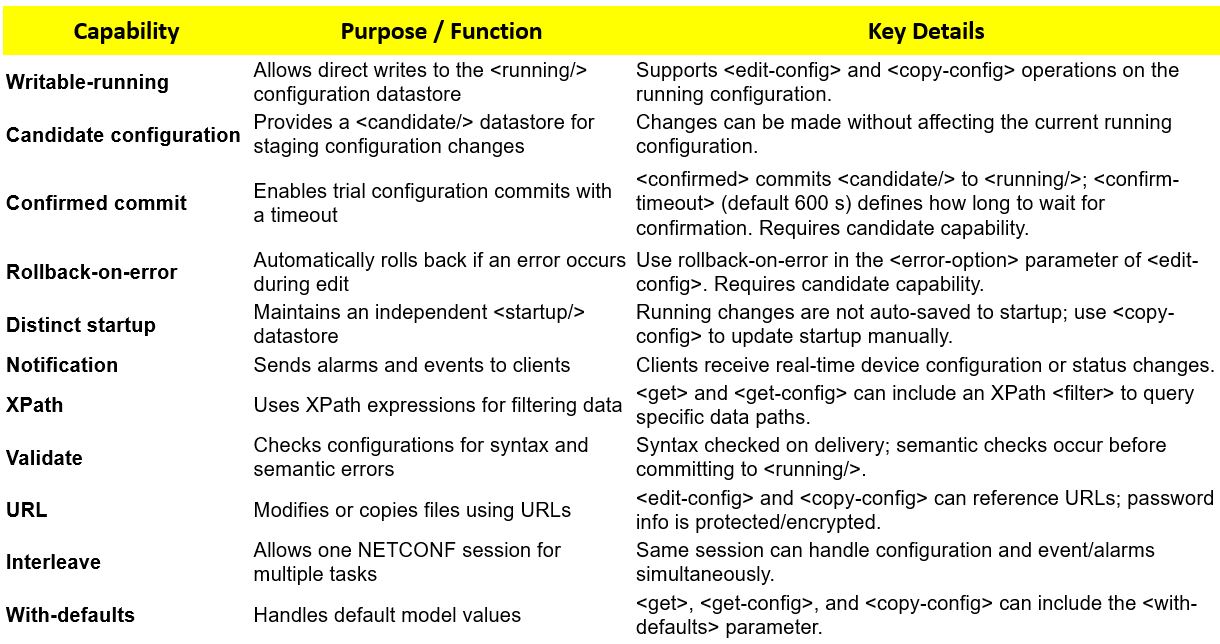
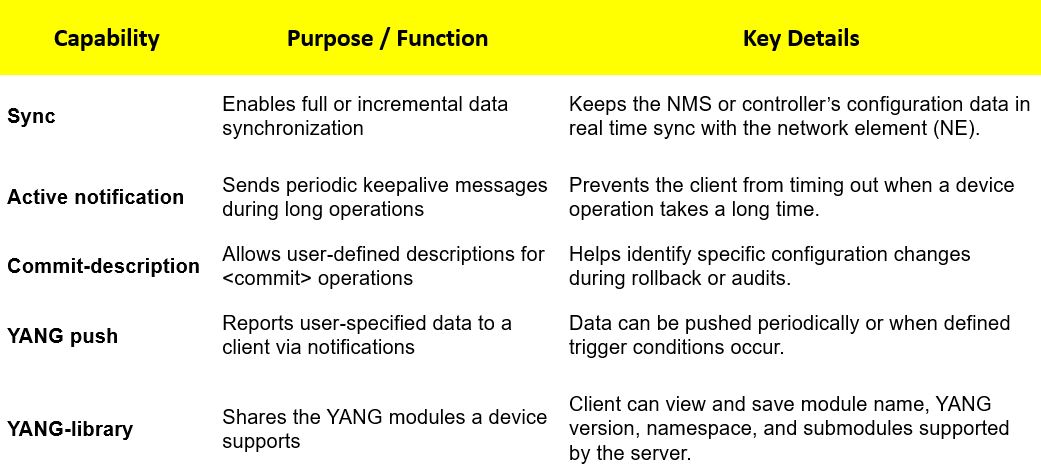
NETCONF Extended Capabilities
In addition to NETCONF-defined capabilities, vendors can customize capabilities to extend management functions.
Related Post
- O1 Interface in Open RAN
- E2 Interface in Open RAN
- Open RAN Network Architecture Components
- What is eCPRI, how it contributes to 5G and Open RAN?
- O-RAN Fronthaul Spilt Option 7-2x
- Section Type in Open RAN Fronthaul
