rApp Introduction
In Open RAN rApp (Remote application) – refer to software applications that do not require low latency or immediate processing. These applications includes functions such as network management, configuration, and administration tasks that do not have strict time requirement. rApps can be run on general-purpose x86 servers, which are typically less expensive and more flexible than specialized hardware.
rApp (Remote application) is a software component that is used to perform functions that are external to the O-RAN architecture, such as interfacing with the core network or connecting to other networks. rApp are typically deployed on top of the CU (Central Unit) and communicates with other components within the O-RAN architecture via the E1 interface.
rApp Key Pointer
- rApps are Non-Real Time AI/ML Application resides within SMO framework
- rApps can be developed and delivered by any third party (Non ORAN Vendors) or Operator can build their own rApps based on own usecases
- rApp communicates to RAN endpoints (O-CU and O-DU) over O1 Interface
- rApp communicates to Near RT-RIC xApps over A1 Interface
- rApps portability and lifecycle management can be done using R1 interface
- rApps runs in the Non-Real-Time RIC i.e. >1 second control loop
- They performs long-term network planning & optimization
- they supports AI/ML model training, enrichment, and inference
- rApps are vendor-agnostic, cloud-native, and microservice-based
- Designed for plug-and-play modularity
- Works in tandem with xAPPs for end-to-end RAN automation
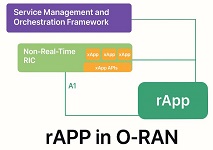
rApp in ORAN Architecture
In ORAN architecture, rAPPs (RAN Intelligent Controller applications) are software programs that run on the Non-Real Time RIC (Non-RT RIC). This Non-RT RIC is a key component in the O-RAN architecture responsible for handling network management and optimization tasks that don’t require immediate, real-time responses.
rAPPs runs on the Non-RT RIC and communicating via the R1 interface and enable intelligent, policy-driven control and optimization of the RAN on a timescale suitable for non-real-time operations.
The R1 interface plays a crucial role here as it serves as the communication pathway between the rAPPs and the underlying Non-RT RIC framework. It enables rAPPs to access necessary data, interact with other components, and ultimately contribute to the overall service management and orchestration of the network.
rApp Interface Connectivity
- Interfacing 5G Core (5G) network: rApp can be used to connect the O-RAN architecture to the core network, allowing the O-RAN architecture to exchange data and signaling with the core network
- Connecting to other networks: rApp can be used to connect the O-RAN architecture to other networks, such as the internet or other wireless networks like WiFi
- Performing Security: rApp can be used to implement security functions, such as authentication and encryption, to protect the O-RAN architecture from threats
- Implementing policy control: rApp can be used to implement policy control functions, such as traffic management and Quality of Service (QoS) control, to optimize the performance of the O-RAN architecture
R1 : Interface between rAPP and Non-Near RT RIC
The R1 interface is a standardized and consistent communication channel between the Non-RT RIC and the rAPPs. It abstracts the complexity of the underlying network while providing a set of services and data that the rAPPs can leverage to enhance RAN performance, support automated network management, and execute non-real-time control functions.
RESTful R1 Service APIs
As many of other application level interfaces, R1 is also based on RESTful mechanism. They enable a variety of essential functions, categorized into the following service domains:
- Service Management and Exposure Services: Service Management and Exposure Services(SME) form a crucial foundation within the O-RAN architecture. They facilitate the dynamic interplay between service providers (rApps) and the Non-RT RIC platform, ensuring efficient service registration, discovery, and real-time updates on service availability.
- Service Registration: This API allows rApps (RAN Intelligent Controller applications) to register the services they offer with the Non-RT RIC (Non-Real Time RAN Intelligent Controller). It’s like a service provider announcing its availability to potential clients.
- Service Discovery: This API enables rApps or other entities to discover the services that have been registered with the Non-RT RIC. It’s akin to a client searching for available service providers.
- Service Events Subscription: This API allows entities to subscribe to notifications about changes in the availability or status of registered services. It’s a way to stay informed about the dynamic service landscape within the O-RAN system.
- Data Management and Exposure Services: Data Management and Exposure Services(DME) play a pivotal role in the O-RAN ecosystem by facilitating the seamless handling of data within the network. It encompasses a suite of APIs designed to streamline the processes of data registration, discovery, and access, ensuring that the right data gets to the right place at the right time.
- Data Registration: Similar to service registration, this API allows entities to register their capability to produce or consume specific types of data.
- Data Discovery: This API enables the discovery of available data types and their producers within the O-RAN system.
- Data Access: Once data types and producers are discovered, this API facilitates the actual access to and retrieval of data. It supports both pull-based (client-initiated) and push-based (server-initiated) data delivery mechanisms.
- RAN Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) Related Services: RAN Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) Related Services are a collection of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that enable the management and upkeep of the Radio Access Network (RAN) within the O-RAN architecture. These services are essential for ensuring the smooth operation, efficient configuration, and timely troubleshooting of the RAN, which is the fundamental infrastructure responsible for connecting user devices to the core network.
- Configuration Management: This API provides functionalities to read and modify configuration data of O-RAN nodes, enabling centralized and efficient management of network configurations.
- Fault Management: This API focuses on handling alarms and fault information within the RAN. It allows for querying alarm details and acknowledging or unacknowledging alarms.
- A1 Related Services: A1 Related Services specifically address the management and orchestration of A1 policies. These policies are instrumental in governing the dynamic interactions and behaviors between the Non-RT RIC and the near-RT RIC . By providing a structured framework for policy creation, modification, and enforcement, A1 Related Services enable intelligent and adaptive control of the RAN, facilitating efficient resource allocation, optimized performance, and support for a wide array of 5G use cases.
- A1 Policy Management: This API enables the creation, retrieval, modification, and deletion of A1 policies. These policies govern the behavior and interactions between the Non-RT RIC and the near-Real-Time RIC, playing a crucial role in intelligent and dynamic control of the RAN.
Common Use Cases of rAPPs
rAPPs are the foundation of intelligent network management within the O-RAN architecture. Operating on the Non-Real Time RIC, rAPPs are specifically designed to handle tasks that don’t demand immediate, real-time responses.
By leveraging their capabilities in data analysis, policy implementation, and automation, rAPPs enables network operators to optimize network performance, enhance energy efficiency, and enable a multitude of innovative use cases, contributing significantly to the evolution of 5G and beyond networks.
Followings is the list of some of the most common use cases of rAPPs
- Network Planning and Deployment: rAPPs can contribute to network planning and deployment processes by providing insights derived from long-term data analysis and network performance monitoring. They can help identify coverage gaps, capacity bottlenecks, and potential areas for optimization or expansion. This information can be invaluable for network operators in making informed decisions regarding network upgrades, new cell deployments, or capacity enhancements.
- Intelligent Automation: rAPPs can automate various network management and optimization tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention and streamlining operations. They can implement intelligent policies, trigger automated responses to network events, and even provide recommendations to network operators based on data-driven insights. This automation can lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and faster response times to network issues.
- Traffic Steering: rAPPs can analyze network traffic patterns, congestion levels, and user demands in a non-real-time manner to make intelligent decisions on how to route traffic. This may involve dynamically adjusting routing paths, load balancing across different cells, or even steering users to different frequency bands or network slices based on their service requirements. By doing so, rAPPs can enhance network performance, reduce congestion, and ensure an optimal quality of experience for users.
- Energy Savings: rAPPs can play a crucial role in energy-saving initiatives within the RAN. They can analyze historical data, traffic patterns, and cell load over longer durations to identify opportunities to put certain network elements into sleep modes or adjust their power levels during periods of low utilization. They can also implement intelligent energy-saving policies based on user behavior and network conditions, contributing to a greener and more sustainable network.
- Anomaly Detection: rAPPs can leverage their access to historical data and machine learning capabilities to identify abnormal patterns or behaviors within the network. This may include detecting sudden spikes in traffic, unusual signaling patterns, or performance degradations that could indicate potential issues or security threats. By detecting these anomalies early on, rAPPs can trigger timely actions, such as alarms, diagnostics, or even automated mitigation steps, to prevent service disruptions and ensure network reliability.
- Long-term Load Balancing: While short-term load balancing is often handled by near-real-time RIC components, rAPPs can excel at long-term load balancing strategies. They can analyze historical load patterns, user mobility trends, and even predictable events (e.g., sports games) to make proactive decisions on resource allocation and cell configuration to avoid congestion and ensure optimal capacity utilization over longer durations.
- Mobility Optimization: rAPPs can enhance user mobility experiences by analyzing mobility patterns and predicting user movements. This can enable them to make proactive handover decisions, pre-allocate resources in anticipated target cells, and optimize mobility parameters to minimize service disruptions during handovers. This can lead to smoother handovers, reduced call drops, and improved quality of service for mobile users.
Input and Output of an rAPP
The primary function of a non-RT RIC rAPP is to intelligently optimize the Radio Access Network (RAN) by analyzing long-term performance insights and adjusting configuration parameters accordingly.
At its core, an rAPP continuously ingests Performance Management (PM) data from the network, processes it using analytics or AI/ML algorithms, and then produces Configuration Management (CM) outputs back to the RAN to enhance performance, efficiency, and user experience.
- How It Works
- Input Stage (PM Data): An rAPP primarily operates by ingesting extensive Performance Management (PM) data collected directly from the RAN, including traffic loads, signal quality indicators, interference levels, user experience metrics, packet-level statistics, and various mobility- or hardware-related events. These inputs offer a comprehensive, long-term view of network performance trends, bottlenecks, anomalies, and patterns across cells and sectors. The input data contents following categories.
-
- O1 Interface Data – PM counters, Fault data, Configuration Data)
- Telemetry / SMO Data Lake – QoE metrics, Traffic trends, Environmental context
- R1 Framework Data Services – ML inference results, Logs and events, Data subscriptions
- A1 Feedback- Policy feedback from Near-RT RIC
-
- Decision Logic: Using policy rules, optimization algorithms, or AI/ML models, the rAPP interprets the input data to identify inefficiencies, congestion, interference issues, poor mobility performance, or capacity hotspots.
- Output Stage (CM Data): Based on the analysis, the rAPP provides primay and seconday outputs. Primary output includes Policies containing Optimization rules, Constraints and Recommendations. Secondary Outputs includes AI/ML model updates, Enrichment information, Analytics reports and Alarms/notifications. Based on these primary and secondary output, the rAPP sends back optimized configuration parameters to the RAN through the non-RT RIC → O1 interface, enabling automated and proactive network tuning. These tuning may include adjustments to transmit power, antenna tilt, handover thresholds, neighbor cell lists, scheduling rules, resource allocation policies, energy-saving configurations, carrier aggregation settings, and transport network parameters. By continuously fine-tuning these configurations, the rAPP ensures optimized coverage, balanced network load, improved handover performance, and enhanced user quality of experience
- Input Stage (PM Data): An rAPP primarily operates by ingesting extensive Performance Management (PM) data collected directly from the RAN, including traffic loads, signal quality indicators, interference levels, user experience metrics, packet-level statistics, and various mobility- or hardware-related events. These inputs offer a comprehensive, long-term view of network performance trends, bottlenecks, anomalies, and patterns across cells and sectors. The input data contents following categories.
Ultimately, the rAPP acts as an autonomous network optimizer, continuously refining the RAN’s behavior to improve coverage, capacity, reliability, and user experience.
Typical Approaches to rAPP Implementation
Implementing an rAPP involves architectural, development, and operational methodologies.
- Approach 1: Microservice-Based Design
- Containerized services (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Language options: Python, Go, Java
- Approach 2: Workflow-Oriented Design
- rAPPs built as workflows orchestrating: Data collection, AI/ML inference, Policy generation and Policy execution
- Approach 3: AI/ML-First Architecture
- Use ML pipelines (training, testing, updating)
- Deploy models to rAPP or Near-RT RIC
- Approach 4: Low-Code/No-Code RAN Automation
- Some vendors offer visual tools where operators can drag-and-drop logic modules to build rAPPs.
- Approach 5: Market-Based Deployment
- Future O-RAN systems expect an rAPP marketplace, allowing plug-and-play apps similar to app stores.
Conclusion
rAPPs are one of the most critical enablers of intelligent, automated, and multi-vendor RAN ecosystems. They provide strategic intelligence, long-term optimization, and AI-driven orchestration capabilities to the O-RAN architecture. With modularity, openness, and cloud-native design, rAPPs are transforming how mobile networks are optimized and managed.
FAQ: rAPP in O-RAN
- Q1. What is the difference between rAPP and xAPP?
- rAPP runs in Non-RT RIC (>1 s timescale)
- xAPP runs in Near-RT RIC (10 ms to 1 s)
- rAPP handles long-term optimization, while xAPP handles real-time actions.
- Q2. What programming languages are used to build rAPPs?
- Most common choices: Python (AI/ML heavy), Go (microservices) and Java (enterprise applications)
- Q3. Does rAPP need AI/ML?
- Not always. Some rAPPs are rule-based, while others use ML for predictions and optimization.
- Q4. What is the role of A1 interface for rAPPs?
- A1 is used for: Policy delivery, Enrichment information, ML model management
- It connects Non-RT RIC (rAPPs) to Near-RT RIC (xAPPs).
- Q5. Can an operator create its own rAPP?
- Yes. O-RAN enables operators to build custom rAPPs for: Coverage tuning, Energy management and Mobility optimization
- Q6. How do rAPPs enable closed-loop automation?
- rAPPs:
- Collect network data,
- Analyze & detect issues,
- Generate A1 policies
- Send policies to Near-RT RIC,
- Get feedback and Continuously refine the system
- rAPPs: